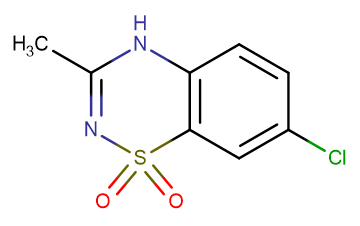
Diazoxide
CAS No. 364-98-7
Diazoxide( NSC 64198 | NSC 76130 | SRG 95213 )
Catalog No. M14255 CAS No. 364-98-7
Diazoxide is a potassium channel activator, which causes local relaxation in smooth muscle by increasing membrane permeability to potassium ions.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 45 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameDiazoxide
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionDiazoxide is a potassium channel activator, which causes local relaxation in smooth muscle by increasing membrane permeability to potassium ions.
-
DescriptionDiazoxide is a potassium channel activator, which causes local relaxation in smooth muscle by increasing membrane permeability to potassium ions.(In Vitro):Diazoxide (Sch-6783) has a number of physiological effects, including lowering the blood pressure and rectifying hypoglycemia. Diazoxide has powerful protective properties against cardiac ischemia.Diazoxide (Sch-6783) could protect NSC-34 neurons against the main sources of neurodegenerative damage. Diazoxide increases Nrf2 nuclear translocation in NSC-34 motoneurons and prevents endogenous oxidative damage. (In Vivo):Diazoxide (Sch-6783) attenuates postresuscitation brain injury, protects mitochondrial function, inhibits brain cell apoptosis, and activates the PKC pathway by opening mitoKATP channels.Treatment with Diazoxide (Sch-6783) in wild-type mice decreases intraocular pressure (IOP) by 21.5±3.2% with an absolute IOP reduction of 3.9 ± 0.6 mm Hg.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsNSC 64198 | NSC 76130 | SRG 95213
-
PathwayEndocrinology/Hormones
-
TargetATPase
-
RecptorNa+/K+-ATPase| Potassium Channel
-
Research AreaCardiovascular Disease
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number364-98-7
-
Formula Weight230.67
-
Molecular FormulaC8H7ClN2O2S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilitySoluble in DMSO
-
SMILESCC1=NS(=O)(=O)C2=C(N1)C=CC(Cl)=C2
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.D’hahan N, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Oct 12;96(21):12162-7.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Blebbistatin
Blebbistatin is a selective non-muscle myosin II (NMII) inhibitor. It promotes directional migration of corneal endothelial cells (CECs) and accelerates wound healing.
-
BTB06584
BTB06584 is a novel acetohydroxyacid synthase(AHAS) inhibitor, a promising drug target against Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB).
-
Liriodendrin
Liriodendrin regulates lung inflammation, the phosphorylation of the NF-kB (p65) and expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF).



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


