BIIB021
CAS No. 848695-25-0
BIIB021( CNF2024 | BIIB-021 | BIIB 021 | CNF 2024 | CNF-2024 )
Catalog No. M16162 CAS No. 848695-25-0
A potent, selective, orally available HSP90 inhibitor with Ki of 1.7 nM for Hsp90α.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 43 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 61 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 97 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 156 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 237 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 405 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 668 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameBIIB021
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionA potent, selective, orally available HSP90 inhibitor with Ki of 1.7 nM for Hsp90α.
-
DescriptionA potent, selective, orally available HSP90 inhibitor with Ki of 1.7 nM for Hsp90α; displays no significant activity against a broad panel of protein kinases, and Na+K+ ATPase; induces the degradation of Hsp90 client proteins including HER-2, AKT, and Raf-1 and upregulates expression of Hsp70 and Hsp27 in tumor cells; inhibits cell growth and induces cell death in cell lines from a variety of tumor types at nanomolar concentrations (IC50=60 nM in N87 cells); exhibits antitumor effects in vivo.Breast Cancer Phase 1 Discontinued(In Vitro):BIIB021 binds in the ATP-binding pocket of Hsp90, interferes with Hsp90 chaperone function, and results in client protein degradation and tumor growth inhibition. BIIB021 inhibits tumor cell (BT474, MCF-7, N87, HT29, H1650, H1299, H69 and H82) proliferation with IC50 from 0.06-0.31 μM. BIIB021 induces the degradation of Hsp90 client proteins including HER-2, Akt, and Raf-1 and up-regulated expression of the heat shock proteins Hsp70 and Hsp27.BIIB021 inhibits Hodgkin's lymphoma cells (KM-H2, L428, L540, L540cy, L591, L1236 and DEV) with IC50 from 0.24-0.8 μM. BIIB021 shows low activity in lymphocytes from healthy individuals. BIIB021 inhibits the constitutive activity of NF-κB despite defective IκB. BIIB021 induces the expression of ligands for the activating NK cell receptor NKG2D on Hodgkin's lymphoma cells resulting in an increased susceptibility to NK cell-mediated killing.BIIB021 enhances the in vitro radiosensitivity of HNSCCA cell lines (UM11B and JHU12) with a corresponding reduction in the expression of key radioresponsive proteins, increases apoptotic cells and enhances G2 arrest.BIIB021 is considerably more active than 17-AAG against adrenocortical carcinoma H295R. The cytotoxic activity of BIIB021 is not influenced by loss of NQO1 or Bcl-2 overexpression, molecular lesions that do not prevent client loss but are nonetheless associated with reduced cell killing by 17-AAG. BIIB021 is also active in 17-AAG resistant cell lines (NIH-H69, MES SA Dx5, NCI-ADR-RES, Nalm6).(In Vivo):Oral administration of BIIB021 leads to tumor growth inhibition in many tumor xenograft models including N87, BT474, CWR22, U87, SKOV3 and Panc-1.BIIB021 effectively inhibits growth of L540cy tumor at a dose of 120 mg/kg. BIIB021 significantly enhances antitumor growth effect of radiation in JHU12 xenograft.
-
In VitroBIIB021 binds in the ATP-binding pocket of Hsp90, interferes with Hsp90 chaperone function, and results in client protein degradation and tumor growth inhibition. BIIB021 inhibits tumor cell (BT474, MCF-7, N87, HT29, H1650, H1299, H69 and H82) proliferation with IC50 from 0.06-0.31 μM. BIIB021 induces the degradation of Hsp90 client proteins including HER-2, Akt, and Raf-1 and up-regulated expression of the heat shock proteins Hsp70 and Hsp27.BIIB021 inhibits Hodgkin's lymphoma cells (KM-H2, L428, L540, L540cy, L591, L1236 and DEV) with IC50 from 0.24-0.8 μM. BIIB021 shows low activity in lymphocytes from healthy individuals. BIIB021 inhibits the constitutive activity of NF-κB despite defective IκB. BIIB021 induces the expression of ligands for the activating NK cell receptor NKG2D on Hodgkin's lymphoma cells resulting in an increased susceptibility to NK cell-mediated killing. BIIB021 enhances the in vitro radiosensitivity of HNSCCA cell lines (UM11B and JHU12) with a corresponding reduction in the expression of key radioresponsive proteins, increases apoptotic cells and enhances G2 arrest.BIIB021 is considerably more active than 17-AAG against adrenocortical carcinoma H295R. The cytotoxic activity of BIIB021 is not influenced by loss of NQO1 or Bcl-2 overexpression, molecular lesions that do not prevent client loss but are nonetheless associated with reduced cell killing by 17-AAG. BIIB021 is also active in 17-AAG resistant cell lines (NIH-H69, MES SA Dx5, NCI-ADR-RES, Nalm6).
-
In VivoOral administration of BIIB021 leads to tumor growth inhibition in many tumor xenograft models including N87, BT474, CWR22, U87, SKOV3 and Panc-1. BIIB021 effectively inhibits growth of L540cy tumor at a dose of 120 mg/kg. BIIB021 significantly enhances antitumor growth effect of radiation in JHU12 xenograft.
-
SynonymsCNF2024 | BIIB-021 | BIIB 021 | CNF 2024 | CNF-2024
-
PathwayCytoskeleton/Cell Adhesion Molecules
-
TargetHSP
-
RecptorHSP90
-
Research AreaCancer
-
IndicationBreast Cancer
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number848695-25-0
-
Formula Weight318.7615
-
Molecular FormulaC14H15ClN6O
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: ≥ 45 mg/mL
-
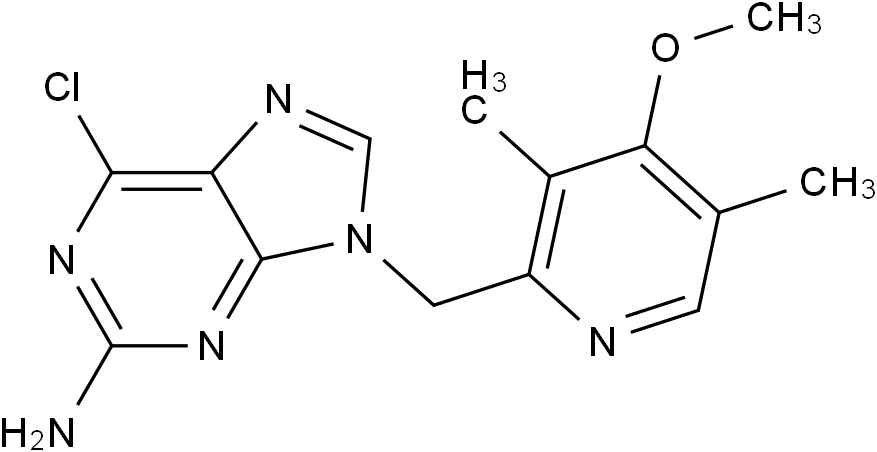
SMILESClC1=C2C(N(CC3=C(C)C(OC)=C(C)C=N3)C=N2)=NC(N)=N1
-
Chemical Name9H-Purin-2-amine, 6-chloro-9-[(4-methoxy-3,5-dimethyl-2-pyridinyl)methyl]-
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Kasibhatla SR, et al. J Med Chem. 2007 Jun 14;50(12):2767-78.
2. Lundgren K, et al. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009 Apr;8(4):921-9.
3. B?ll B, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2009 Aug 15;15(16):5108-16.
4. Gopalakrishnan R, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Sep 15;19(18):5016-26.
molnova catalog



related products
-
HSP27 inhibitor J2
HSP27 inhibitor J2 is a small molecule functional inhibitor of Hsp27.
-
Arimoclomol maleate
Arimoclomol maleate (BRX-220) is a heat shock protein (HSP) co-inducer.
-
KUNG38
A potent, selective Grp94 inhibitor with Kd of 0.44 uM; displays 19-fold selecticity over Hsp90α.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


