Avadomide
CAS No. 1015474-32-4
Avadomide( CC-122 )
Catalog No. M10081 CAS No. 1015474-32-4
A small molecule that binds to cereblon (CRBN) and promotes degradation of Aiolos and Ikaros in DLBCL and T cells in vitro and in vivo.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 43 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 69 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 113 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 207 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 332 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 494 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameAvadomide
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionA small molecule that binds to cereblon (CRBN) and promotes degradation of Aiolos and Ikaros in DLBCL and T cells in vitro and in vivo.
-
DescriptionA small molecule that binds to cereblon (CRBN) and promotes degradation of Aiolos and Ikaros in DLBCL and T cells in vitro and in vivo; induces degradation of transcription factors Aiolos (IKZF3) and Ikaros (IKZF1) and does not affect CK1α protein levels; inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in a broad panel of DLBCL cell lines, and stimulates IL-2 production in primary T cells; reduces tumor growth in xenograft models established from ABC- and GCB-DLBCL cell lines,Blood Cancer Approved(In Vitro):Avadomide inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in ABC and GCB DLBCL. In DLBCL cell lines, Avadomide-induced degradation or short hairpin RNA-mediated knockdown of Aiolos and Ikaros correlates with increased transcription of IFN-stimulated genes independent of IFN-α, -β, and -γ production and/or secretion and results in apoptosis in both activated B-cell (ABC) and germinal center B-cell DLBCL. (In Vivo):Treatment of female CB-17 SCID mice with Avadomide (CC122) at 3 or 30 mg/kg once daily significantly decreased tumor growth in OCI-LY10 ABC-DLBCL (P = .028 and P < .001, respectively) and WSU-DLCL2 GCB-DLBCL derived xenograft models (P < .01) compared with the vehicle control. In a separate study, we assessed the ability of Avadomide (CC122) to promote degradation of Ikaros and Aiolos in vivo. In the 21-day efficacy study of WSU-DLCL2 xenograft transplanted mice, tumors were excised 1, 6, or 24 hours post final dosing. Aiolos and Ikaros expression was interrogated through immunohistochemistry (IHC) and was found to be decreased 64% and 30%, respectively, compared with vehicle within 1 hour of treatment, with a maximal reduction of 94% and 69%, respectively, observed at 6 hours. Aiolos and Ikaros levels partially recovered 24 hours postdosing with protein level within 20% and 34% of vehicle, respectively. The 24-hour postdose Aiolos and Ikaros expression represents the trough compound level following multiple doses of Avadomide (CC122). When the 1-hour time point is compared with the 24-hour postdose time point, there is a significant reduction in Aiolos but not Ikaros expression; however, at the 6-hour time point, both transcription factors are significantly different from the 24-hour time point. Taken together, these data reveal that Avadomide (CC122) inhibited DLBCL tumor growth in vivo and that this activity was associated with the degradation of Aiolos and Ikaros in both ABC- and GCB-DLBCL xenograft models.
-
In VitroAvadomide inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in ABC and GCB DLBCL. In DLBCL cell lines, Avadomide-induced degradation or short hairpin RNA-mediated knockdown of Aiolos and Ikaros correlates with increased transcription of IFN-stimulated genes independent of IFN-α, -β, and -γ production and/or secretion and results in apoptosis in both activated B-cell (ABC) and germinal center B-cell DLBCL.
-
In VivoTreatment of female CB-17 SCID mice with Avadomide (CC122) at 3 or 30 mg/kg once daily significantly decreased tumor growth in OCI-LY10 ABC-DLBCL (P = .028 and P < .001, respectively) and WSU-DLCL2 GCB-DLBCL derived xenograft models (P < .01) compared with the vehicle control. In a separate study, we assessed the ability of Avadomide (CC122) to promote degradation of Ikaros and Aiolos in vivo. In the 21-day efficacy study of WSU-DLCL2 xenograft transplanted mice, tumors were excised 1, 6, or 24 hours post final dosing. Aiolos and Ikaros expression was interrogated through immunohistochemistry (IHC) and was found to be decreased 64% and 30%, respectively, compared with vehicle within 1 hour of treatment, with a maximal reduction of 94% and 69%, respectively, observed at 6 hours. Aiolos and Ikaros levels partially recovered 24 hours postdosing with protein level within 20% and 34% of vehicle, respectively. The 24-hour postdose Aiolos and Ikaros expression represents the trough compound level following multiple doses of Avadomide (CC122). When the 1-hour time point is compared with the 24-hour postdose time point, there is a significant reduction in Aiolos but not Ikaros expression; however, at the 6-hour time point, both transcription factors are significantly different from the 24-hour time point. Taken together, these data reveal that Avadomide (CC122) inhibited DLBCL tumor growth in vivo and that this activity was associated with the degradation of Aiolos and Ikaros in both ABC- and GCB-DLBCL xenograft models.
-
SynonymsCC-122
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetE3 Ubiquitin Ligase
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research AreaCancer
-
IndicationBlood cancer
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1015474-32-4
-
Formula Weight286.2859
-
Molecular FormulaC14H14N4O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: ≥ 33 mg/mL
-
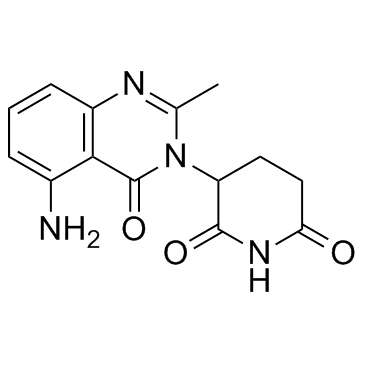
SMILESCC1=NC2=CC=CC(=C2C(=O)N1C3CCC(=O)NC3=O)N
-
Chemical Name2,6-Piperidinedione, 3-(5-amino-2-methyl-4-oxo-3(4H)-quinazolinyl)-
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Hagner PR, et al. Blood. 2015 Aug 6;126(6):779-89.
2. Kr?nke J, et al. Nature. 2015 Jul 9;523(7559):183-188.
3. Chamberlain PP, et al. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2014 Sep;21(9):803-9.
4. Koeller KM, et al. Chem Biol. 2003 May;10(5):397-410.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Tasisulam sodium
Tasisulam (LY 573636) is a small molecule antitumor agent that induces apoptosis via the intrinsic pathway.
-
BRD5529
BRD5529 is a small-molecule inhibitor that disrupts the interaction of CARD9-E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM62 with IC50 of 8.6 uM.
-
SPOP-IN-6b
SPOP-IN-6b is a potent, small-molecule E3 Ligase adaptor SPOP (speckle-type POZ protein) inhibitor.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


