SW-106065
CAS No. 62289-81-0
SW-106065( SW106065 | MPNST-IN-21 )
Catalog No. M15357 CAS No. 62289-81-0
SW-106065 is a novel pharmacologic inducer of apoptosis in MPNST (malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 57 | Get Quote |


|
| 5MG | 98 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 155 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 282 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 444 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 653 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | 1368 | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameSW-106065
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionSW-106065 is a novel pharmacologic inducer of apoptosis in MPNST (malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors).
-
DescriptionSW-106065 is a novel pharmacologic inducer of apoptosis in MPNST (malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors); inhibits ATP consumption of sMPNST and other models of MPNST with EC50 of 1 uM, shows no toxicity to normally dividing Schwann cells or mouse embryonic fibroblasts; reduces MPNST burden in a mouse allograft model.
-
In VitroSW106065 (Compound 21, Cpd21) inhibits the human MPNST cell lines growth in a dose-dependent manner, and EC50 concentrations of 439 nM and 753.6 nM for S462 and SNF96.2 cells, respectively. SW106065 remains nontoxic to normally dividing Schwann cells or mouse embryonic fibroblasts.SW106065 (Cpd21; 0.25-5 μM; 24 hours; sMPNST cells) treatment shows a decreased percentage of cells in S phase, and a corresponding increased percentage in G1/G0 and G2/M. SW106065 (Cpd21; 0.25-5 μM; 24 hours; sMPNST cells) treatment decreases the levels of cyclin A2, cyclin B1, cyclin D1, cyclin E, cdk4, and cdk6. And increases levels of cdkn1a and cdkn2a mRNA were observed in a dose-dependent manner.SW106065 (Cpd21; 0.25-5 μM; 24 hours; sMPNST cells) treatment decreases the levels of Cyclin D1 protein.SW106065 (Cpd21) treatment significant increase in the percentage of apoptotic cells. Cell Cycle Analysis Cell Line:sMPNST cells Concentration:0.25 μM, 0.5 μM, 1 μM, 2.5 μM, and 5 μM Incubation Time:24 hours Result:Showed a decreased percentage of cells in S phase, and a corresponding increased percentage in G1/G0 and G2/M.RT-PCR Cell Line:sMPNST cells Concentration:0.25 μM, 0.5 μM, 1 μM, 2.5 μM, and 5 μM Incubation Time:24 hours Result:Decreased levels of cyclin A2, cyclin B1, cyclin D1, cyclin E, cdk4, and cdk6. Increased levels of cdkn1a and cdkn2a mRNA were observed in a dose-dependent manner.Western Blot Analysis Cell Line:sMPNST cells Concentration:0.25 μM, 0.5 μM, 1 μM, 2.5 μM, and 5 μMIncubation Time:24 hoursResult:Decreased levels of Cyclin D1 protein.
-
In VivoSW106065 (Cpd21; 40 mg/kg; intraperitoneal injection; twice per day for 4 weeks) treatment can be delivered to mice in concentrations to sufficiently penetrate sMPNST tissue, and inhibit tumor development. Animal Model:NCR-nu/nu female mice (6-7 week old) injected with MPNST cells Dosage:40 mg/kg Administration:Intraperitoneal injection; twice per day for 4 weeks Result:Reduced MPNST burden in a mouse allograft model.
-
SynonymsSW106065 | MPNST-IN-21
-
PathwayApoptosis
-
TargetApoptosis
-
RecptorApoptosis
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number62289-81-0
-
Formula Weight204.247
-
Molecular FormulaC10H8N2OS
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (489.60 mM)
-
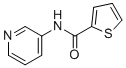
SMILESC1=CC(=CN=C1)NC(=O)C2=CC=CS2
-
Chemical NameN-(pyridin-3-yl)thiophene-2-carboxamide
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Chau V, et al. Cancer Res. 2014 Jan 15;74(2):586-97.
molnova catalog



related products
-
AP-III-a4 hydrochlor...
AP-III-a4 (ENOblock) hydrochloride is a nonsubstrate analogue enolase inhibitor with an IC50 of 0.576 uM. AP-III-a4 hydrochloride can be used for the research of cancer and diabetic.
-
Taurodeoxycholic aci...
Taurodeoxycholic acid (Taurodeoxychloic acid) is a bile acid taurine conjugate of deoxycholic acid, a human metabolite that stabilizes mitochondrial membranes and reduces the formation of free radicals.
-
Epimedokoreanin B
Epimedokoreanin B (EKB), an isoprenylated flavonoid isolated from Korean Epimedium, exhibited anticancer activity in human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) A549 and NCI-H292 cells.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


