Nonivamide
CAS No. 2444-46-4
Nonivamide( Pseudocapsaicin | Pelargonic acid vanillylamide | Nonanoic acid vanillylamide )
Catalog No. M13707 CAS No. 2444-46-4
A capsaicin analog that acts as an agonist of TRPV1 channel.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 45 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 61 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameNonivamide
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionA capsaicin analog that acts as an agonist of TRPV1 channel.
-
DescriptionA capsaicin analog that acts as an agonist of TRPV1 channel; causes calcium release from the ER and alters the transcription of GADD153, GADD45alpha, GRP78/BiP, ATF3, CCND1, and CCNG2 in human bronchial epithelial and alveolar cells; stimulates the Ca(2+)-dependent release of serotonin and dopamine in SH-SY5Y cells at 1 uM; also enhances miRNA let-7d expression and decreases adipogenesis PPARγ expression in 3T3-L1 cells.Pain Phase 3 Clinical(In Vitro):Nonivamide, a synthetic derivate of natural capsaicin, has an effective antifouling activity. Capsaicin exhibits 4d-EC50 values of 5.5±0.5 mg/L, 23±2 mg/L, 6.9±0.2 mg/L, and 15.6±0.4 mg/L in static toxicity tests conducted using Pseudomonas putida, Lake Erie bacteria, Vibrio natriegens, and Vibrio parahaemolyticus, respectively. A significant growth inhibitory effect (p<0.01) is observed in the group treated with 1 mg/L of Nonivamide for 4 d, and the EC50 value (4 d-EC50) is 5.1 mg/L. Nonivamide treatment causes calcium release from the ER and altered the transcription of growth arrest- and DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 (GADD153), GADD45α, GRP78/BiP, ATF3, CCND1, and CCNG2) in a manner comparable with prototypical ER stress-inducing agents. ER calcium flux is evaluated by pretreating cells with 2.5 μM thapsigargin for 5 min followed by addition of 2.5 μM Nonivamide. Treatment of TRPV1-overexpressing cells with 2.5 μM Nonivamide produces marked increases in cytosolic calcium due to release of calcium from ER stores. Treatment of TRPV1-overexpressing cells with 1 μM Nonivamide causes an approximate 50% loss in cell viability after a 24-h period. BEAS-2B cells treated with 100 and 200 μM Nonivamide also exhibits a shift in the relative amount of EIF2α-P and an increase in the expression of GADD153 mRNA and protein. Treatment with Nonivamide reduces lipid accumulation to a similar extent as CAP; the effects are not different from the effects after CAP treatment at any of the tested concentrations. Compared to untreated control cells, treatment with Nonivamide decreases lipid accumulation by 5.34±1.03% (P<0.05) at 0.01 μM up to 10.4±2.47% (P<0.001) at 1 μM.
-
In VitroNonivamide, a synthetic derivate of natural capsaicin, has an effective antifouling activity. Capsaicin exhibits 4d-EC50 values of 5.5±0.5 mg/L, 23±2 mg/L, 6.9±0.2 mg/L, and 15.6±0.4 mg/L in static toxicity tests conducted using Pseudomonas putida, Lake Erie bacteria, Vibrio natriegens, and Vibrio parahaemolyticus, respectively. A significant growth inhibitory effect (p<0.01) is observed in the group treated with 1 mg/L of Nonivamide for 4 d, and the EC50 value (4 d-EC50) is 5.1 mg/L. Nonivamide treatment causes calcium release from the ER and altered the transcription of growth arrest- and DNA damage-inducible transcript 3 (GADD153), GADD45α, GRP78/BiP, ATF3, CCND1, and CCNG2) in a manner comparable with prototypical ER stress-inducing agents. ER calcium flux is evaluated by pretreating cells with 2.5 μM thapsigargin for 5 min followed by addition of 2.5 μM Nonivamide. Treatment of TRPV1-overexpressing cells with 2.5 μM Nonivamide produces marked increases in cytosolic calcium due to release of calcium from ER stores. Treatment of TRPV1-overexpressing cells with 1 μM Nonivamide causes an approximate 50% loss in cell viability after a 24-h period. BEAS-2B cells treated with 100 and 200 μM Nonivamide also exhibits a shift in the relative amount of EIF2α-P and an increase in the expression of GADD153 mRNA and protein. Treatment with Nonivamide reduces lipid accumulation to a similar extent as CAP; the effects are not different from the effects after CAP treatment at any of the tested concentrations. Compared to untreated control cells, treatment with Nonivamide decreases lipid accumulation by 5.34±1.03% (P<0.05) at 0.01 μM up to 10.4±2.47% (P<0.001) at 1 μM.
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsPseudocapsaicin | Pelargonic acid vanillylamide | Nonanoic acid vanillylamide
-
PathwayMembrane Transporter/Ion Channel
-
TargetTRP/TRPV Channel
-
RecptorTRPV1
-
Research AreaNeurological Disease
-
IndicationPain
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2444-46-4
-
Formula Weight293.4012
-
Molecular FormulaC17H27NO3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility10 mM in DMSO
-
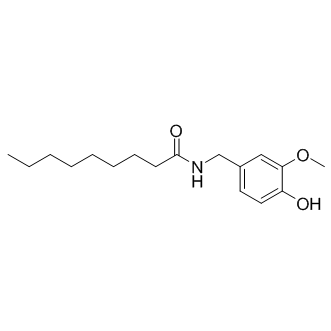
SMILESO=C(NC(CCCCCCCC)=O)C1=CC=C(O)C(OC)=C1
-
Chemical NameNonanamide, N-[(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Rohm B, et al. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2013 Nov;57(11):2008-18.
2. Thomas KC, et al. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007 Jun;321(3):830-8.
3. Rohm B, et al. J Cell Biochem. 2015 Jun;116(6):1153-63.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Pico145
Pico145 is a remarkable inhibitor of TRPC1/4/5 channels. Pico145 inhibits (?)-englerin A-activated TRPC4/TRPC5 channels.
-
AMG-9810
A potent, selective and competitive TRPV1 antagonist with IC50 of 24.5 and 85.6 nM for human and rat TRPV1, repectively.
-
Oleoyl Serotonin
Oleoyl Serotonin is an antagonist of hTRPV1 with an IC50 of 2.57 μM.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


