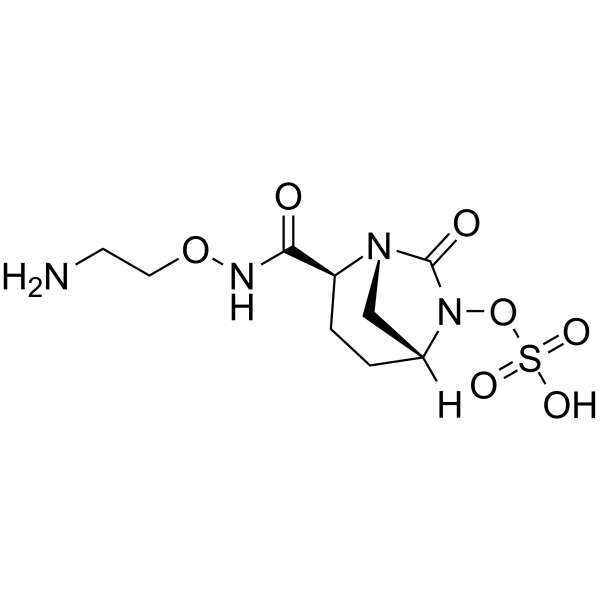
Nacubactam
CAS No. 1452458-86-4
Nacubactam( OP0595 free acid )
Catalog No. M26321 CAS No. 1452458-86-4
Nacubactam is a potent inhibitor of non-β-lactam-β-lactamase with activity against class A and class C β-lactamases.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 115 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 195 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 392 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 590 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 839 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameNacubactam
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionNacubactam is a potent inhibitor of non-β-lactam-β-lactamase with activity against class A and class C β-lactamases.
-
DescriptionNacubactam is a potent inhibitor of non-β-lactam-β-lactamase with activity against class A and class C β-lactamases.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsOP0595 free acid
-
PathwayGPCR/G Protein
-
TargetAntibacterial
-
RecptorHuman Endogenous Metabolite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1452458-86-4
-
Formula Weight324.31
-
Molecular FormulaC9H16N4O7S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 250 mg/mL (770.87 mM)
-
SMILESNCCONC(=O)[C@@H]1CC[C@@H]2CN1C(=O)N2OS(O)(=O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Stitt A, et al. The AGE inhibitor pyridoxamine inhibits development of retinopathy in experimental diabetes. Diabetes. 2002 Sep;51(9):2826-32.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Carvacrol methyl eth...
Carvacrol methyl ether is derived from plant volatile oil and exhibits antibacterial activity.
-
AAI-101
AAI-101 is a novel extended-spectrum β-lactamase inhibitor with activity against many β-lactamases, including some class A and class D carbapenemases.
-
F1063-0967
F1063-0967 is a Dual-specificity phosphatase 26 (DUSP26) inhibitor with an IC50 of 11.62 μM.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


