NU-6300
CAS No. 2070015-09-5
NU-6300( NU 6300 | NU6300 )
Catalog No. M13220 CAS No. 2070015-09-5
NU-6300 is the first covalent, irreversible, ATP-Competitive CDK2 inhibitor with Ki of 6 nM.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 312 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 1341 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 1791 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameNU-6300
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionNU-6300 is the first covalent, irreversible, ATP-Competitive CDK2 inhibitor with Ki of 6 nM.
-
DescriptionNU-6300 is the first covalent, irreversible, ATP-Competitive CDK2 inhibitor with Ki of 6 nM; shows modest effect (GI50=8 uM) against human MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells; inhibits Rb phosphorylation in Rb-positive SKUT-1B cells.
-
In VitroNU6300 (50 μM; 0-1 hour) covalently modifies and irreversible inhibits CDK2.Western Blot Analysis Cell Line:SKUT-1B cells Concentration:50 μM Incubation Time:0-1 hour Result:Affected retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein (Rb) phosphorylation in SKUT-1B cells and covalently binded with CDK2.
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsNU 6300 | NU6300
-
PathwayAngiogenesis
-
TargetCDK
-
RecptorCDK
-
Research AreaCancer
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2070015-09-5
-
Formula Weight413.4933
-
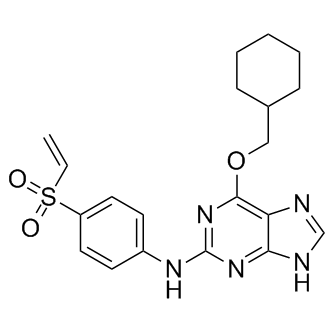
Molecular FormulaC20H23N5O3S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: ≥ 32 mg/mL
-
SMILESO=S(C1=CC=C(NC2=NC(OCC3CCCCC3)=C4N=CNC4=N2)C=C1)(C=C)=O
-
Chemical Name6-(cyclohexylmethoxy)-N-(4-(vinylsulfonyl)phenyl)-9H-purin-2-amine
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Anscombe E, et al. Chem Biol. 2015 Sep 17;22(9):1159-64.
molnova catalog



related products
-
SU-9516
A selective CDK2 inhibitor with IC50 of 22 nM; shows less potent for CDK1/CDK4(IC50=40/200 nM), no inhibition on PKC, EGFR, p38MAPK; decreases the phosphorylation of pRb, and increases caspase-3 activation.
-
Amsilarotene
Amsilarotene inhibits the phosphorylation of retinoblastoma gene product (RB) and increases the presence of 2 cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK) inhibitors resulting in cell cycle arrest.
-
NU-2058
An ATP-competitive inhibitor of CDK1 and CDK2 with Ki of 5 uM and 12 uM respectively; inhibits human tumor cells with a mean GI50 of 13±7 uM.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


