NSC49652
CAS No. 908563-68-8
NSC49652( —— )
Catalog No. M34352 CAS No. 908563-68-8
NSC49652 triggers apoptotic cell death dependent on p75NTR and JNK activity in neurons and melanoma cells, and inhibits tumor growth in a melanoma mouse model.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 47 | Get Quote |


|
| 5MG | 68 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 116 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 227 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 361 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 530 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | 1152 | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameNSC49652
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionNSC49652 triggers apoptotic cell death dependent on p75NTR and JNK activity in neurons and melanoma cells, and inhibits tumor growth in a melanoma mouse model.
-
DescriptionNSC49652 is a reversible, orally active p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR, also known as NGFR, TNFRSF16, and CD271) agonist. NSC49652 targets the transmembrane domain of p75NTR. NSC49652 induces apoptosis and affects the viability of melanoma cells.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayApoptosis
-
TargetApoptosis
-
RecptorApoptosis
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number908563-68-8
-
Formula Weight225.24
-
Molecular FormulaC14H11NO2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : ≥ 20.83 mg/mL (92.48 mM; )
-
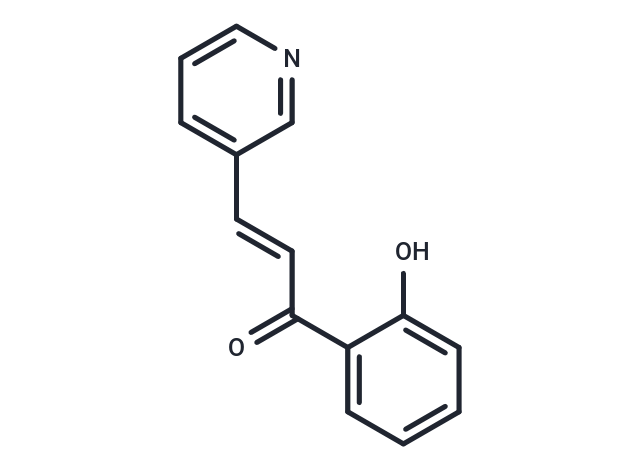
SMILESOc1ccccc1C(=O)\C=C\c1cccnc1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Goh ETH, et al. A Small Molecule Targeting the Transmembrane Domain of Death Receptor p75NTR Induces Melanoma Cell Death and Reduces Tumor Growth. Cell Chem Biol. 2018 Dec 20;25(12):1485-1494.e5.?
molnova catalog



related products
-
Ginsenoside Rg6
Ginsenoside Rg6 inhibits the proliferation and induces apoptosis of human lymphoma JK cells
-
UCF 101
UCF 101 is a specific inhibitor of HtrA2 and reduces apoptosis in PC12 cells.
-
Lupiwighteone
Lupiwighteone has anti-angiogenesis potential, it also has anticancer and cancer preventive effects on SH-SY5Y cells.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


