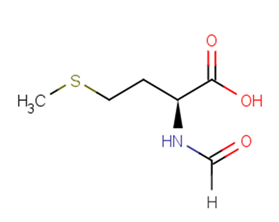
N-Formyl-L-methionine
CAS No. 4289-98-9
N-Formyl-L-methionine( fMet )
Catalog No. M19603 CAS No. 4289-98-9
Effective in the initiation of protein synthesis. The initiating methionine residue enters the ribosome as N-formyl methionyl tRNA. This process occurs in Escherichia coli and other bacteria as well as in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 500MG | 69 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameN-Formyl-L-methionine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionEffective in the initiation of protein synthesis. The initiating methionine residue enters the ribosome as N-formyl methionyl tRNA. This process occurs in Escherichia coli and other bacteria as well as in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells.
-
DescriptionEffective in the initiation of protein synthesis. The initiating methionine residue enters the ribosome as N-formyl methionyl tRNA. This process occurs in Escherichia coli and other bacteria as well as in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsfMet
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number4289-98-9
-
Formula Weight177.22
-
Molecular FormulaC6H11NO3S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:10 mM
-
SMILESCSCC[C@H](NC=O)C(O)=O
-
Chemical Nameformyl-L-methionine
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Sherriff RM et al. Isolation and purification of N-formylmethionine aminopeptidase from rat intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Mar 12;1119(3):275-80.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Somatostatin-25
Somatostatin is an endogenous neuropeptide hormone found in the brain and pancreas. Somatostatin binds several isoforms of the somatostatin receptor, exhibiting anxiolytic, antiepileptic/anticonvulsant, and anorexigenic activities.
-
LDC000067
LDC000067 is a highly specific and selective CDK9 inhibitor with an IC50 value of 44±10 nM.
-
Unifiram
Unifiram is a cognition-enhancer. Unifiram induces a long-lasting increase in the amplitude of field excitatory postsynaptic potentials (fEPSPs) in the rat hippocampal CA1 region (EC50= 27 nM) and increases acetylcholine (ACh) release in the rat cerebral cortex.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


