Equilin
CAS No. 474-86-2
Equilin( —— )
Catalog No. M33216 CAS No. 474-86-2
Equilin (7-Dehydroestrone) is a neurotrophic estrogenic steroid with vasodilatory activity that increases monocyte-endothelial adhesion through NF-κB signalling.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 105 | Get Quote |


|
| 5MG | 59 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 97 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameEquilin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionEquilin (7-Dehydroestrone) is a neurotrophic estrogenic steroid with vasodilatory activity that increases monocyte-endothelial adhesion through NF-κB signalling.
-
DescriptionEquilin (7-Dehydroestrone) is an important member of the large group of oestrogenic substances and is chemically related to menformon (oestrone). Equilin increases the growth of cortical neurons via an NMDA receptor-dependent mechanism.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayGPCR/G Protein
-
TargetCalcium Channel
-
RecptorCalcium Channel
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number474-86-2
-
Formula Weight268.35
-
Molecular FormulaC18H20O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (372.65 mM; Ultrasonic )
-
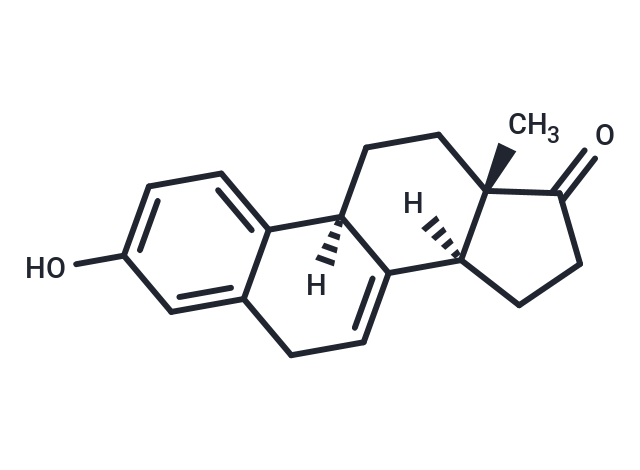
SMILES[H][C@@]12CCC(=O)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@@]1([H])C2=CCc2cc(O)ccc12
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. David K, et al. Some biological properties of equilin. Biochem J. 1935;29(2):371-377.?
molnova catalog



related products
-
Ethyl cinnamate
Ethyl cinnamate has antifungal, and vasorelaxant effects. Ethyl cinnamate can lead to the damage of cell membrane system and metabolic disorder through inducing lipid peroxidation via initiating ROS overproduction.
-
Imagabalin
Imagabalin (PD 0332334) is a novel ligand for the α2δ subunit of the voltage-dependent calcium channel (VDCC) with some selectivity for the α2δ1 subunit over α2δ2.
-
Norverapamil hydroch...
A calcium channel blocker and the main active metabolite of verapamil.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


