KN-93
CAS No. 139298-40-1
KN-93( —— )
Catalog No. M17274 CAS No. 139298-40-1
KN-93 is a selective inhibitor of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CaMKII), competitively blocking CaM binding to the kinase.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 123 | In Stock |


|
| 2MG | 68 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 109 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 149 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 306 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 369 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 541 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameKN-93
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionKN-93 is a selective inhibitor of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CaMKII), competitively blocking CaM binding to the kinase.
-
DescriptionKN-93 is a selective inhibitor of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CaMKII), competitively blocking CaM binding to the kinase.(In Vitro):After 2 days of KN-93 treatment, 95% of cells are arrested in G1. G1 arrest is reversible; 1 day after KN-93 release, a peak of cells had progressed into S and G2-M. KN-93 also blocks cell growth stimulated by basic fibroblast growth factor, platelet-derived growth factor-BB, and epidermal growth factor in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts. KN-93 inhibits the H+, K+-ATPase activity but strongly dissipates the proton gradient formed in the gastric membrane vesicles and reduces the volume of luminal space. KN-93 (0.5 μM) prevents increased LV developed pressure during action potential prolongation and early afterdepolarizations. Ca2+-independent CaM kinase activity is increased during early afterdepolarizations and this increase is prevented by KN-93. KN-93 (10 μM )significantly inhibits the activation of CaMKII/NF-κB signaling induced by elevated glucose, and subsequently decreases the expression of VEGF, iNOS and ICAM-1 in Müller cells.(In Vivo):KN-93 (1 mg/kg/day, i.p.) inhibits retinal vascular leakage induced by diabetes, and suppresses phosphorylation of CaMKII and NF-κB in diabetic retina.
-
In VitroAfter 2 days of KN-93 treatment, 95% of cells are arrested in G1. G1 arrest is reversible; 1 day after KN-93 release, a peak of cells had progressed into S and G2-M. KN-93 also blocks cell growth stimulated by basic fibroblast growth factor, platelet-derived growth factor-BB, and epidermal growth factor in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts. KN-93 inhibits the H+, K+-ATPase activity but strongly dissipates the proton gradient formed in the gastric membrane vesicles and reduces the volume of luminal space. KN-93 (0.5 μM) prevents increased LV developed pressure during action potential prolongation and early afterdepolarizations. Ca2+-independent CaM kinase activity is increased during early afterdepolarizations and this increase is prevented by KN-93. KN-93 (10 μM )significantly inhibits the activation of CaMKII/NF-κB signaling induced by elevated glucose, and subsequently decreases the expression of VEGF, iNOS and ICAM-1 in Müller cells.
-
In VivoKN-93 (1 mg/kg/day, i.p.) inhibits retinal vascular leakage induced by diabetes, and suppresses phosphorylation of CaMKII and NF-κB in diabetic retina.
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetTyrosinase
-
RecptorCaMK
-
Research AreaCancer
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number139298-40-1
-
Formula Weight501.04
-
Molecular FormulaC26H29ClN2O4S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO : ≥ 50 mg/mL. 99.79 mM
-
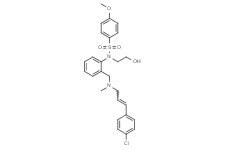
SMILESO=S(=O)(c1ccc(OC)cc1)N(c1ccccc1CN(C/C=C/c1ccc(cc1)Cl)C)CCO
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Tombes RM, et al. Cell Growth Differ. 1995 Sep;6(9):1063-70.
molnova catalog



related products
-
SU 5616
SU 5616 (WAY-608241) regulates abnormal cell proliferation and modulates tyrosine kinase signaling.
-
lysine
Lysine is one of nine essential amino acids in humans required for growth and tissue repair, Lysine is supplied by many foods, especially red meats, fish, and dairy products.
-
4-Butylresorcinol
4-Butylresorcinol is a potent inhibitor of tyrosinase(IC50 : 11.27 μM) and is used in cosmetics as a depigmenting agent.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


