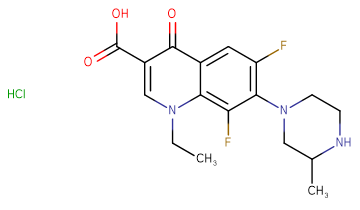
Lomefloxacin
CAS No. 98079-51-7
Lomefloxacin( —— )
Catalog No. M16889 CAS No. 98079-51-7
Lomefloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, used to treat bacterial infections including bronchitis and urinary tract infections.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 25MG | 34 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 49 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 61 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameLomefloxacin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionLomefloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, used to treat bacterial infections including bronchitis and urinary tract infections.
-
DescriptionLomefloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, used to treat bacterial infections including bronchitis and urinary tract infections. It is also used to prevent urinary tract infections prior to surgery.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayCell Cycle/DNA Damage
-
TargetTopoisomerase
-
RecptorTopo II| Topo IV
-
Research AreaInfection
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number98079-51-7
-
Formula Weight351.35
-
Molecular FormulaC17H19F2N3O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilitySoluble in Water
-
SMILESCl.CCN1C=C(C(O)=O)C(=O)C2=CC(F)=C(N3CCNC(C)C3)C(F)=C12
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Takenouchi T, et al. Antimicrob Agents ChemOthers. 1995 Jul;39(7):1414-8
molnova catalog



related products
-
Groenlandicine
Groenlandicine is a protoberberine alkaloid from Coptidis Rhizoma. Groenlandicine exhibits moderate inhibitory effect with IC50 value of 154.2 μM for human recombinant aldose reductase (HRAR).
-
Leurubicin
Leurubicin (N-Leucyldoxorubicin) is a potential Top II inhibitor for the study of bacterial infections .
-
Nifurpirinol
Nifurpirinol (P-7138) is an antimicrobial compound that is acutely toxic to milkfish (Chanos chanos) species.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


