Inh2-B1
CAS No. 690216-38-7
Inh2-B1( STK1 inhibitor B1 )
Catalog No. M15641 CAS No. 690216-38-7
Inh2-B1 (STK1 inhibitor B1) is a novel specific S aureus Ser/Thr protein kinase (STK1) inhibitor with IC50 of 49 uM.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameInh2-B1
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionInh2-B1 (STK1 inhibitor B1) is a novel specific S aureus Ser/Thr protein kinase (STK1) inhibitor with IC50 of 49 uM.
-
DescriptionInh2-B1 (STK1 inhibitor B1) is a novel specific S aureus Ser/Thr protein kinase (STK1) inhibitor with IC50 of 49 uM, directly binds to ATP-binding catalytic domain; exhibits in vitro growth inhibition of MRSA, and in vivo protection in mice against the lethal MRSA challenge; down-regulates cell wall hydrolase genes and disrupts the biofilm formation of MRSA.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsSTK1 inhibitor B1
-
PathwayGPCR/G Protein
-
TargetAntibacterial
-
RecptorAntibacterial
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number690216-38-7
-
Formula Weight411.45
-
Molecular FormulaC19H13N3O4S2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILES——
-
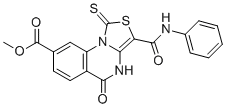
Chemical NameMethyl 5-oxo-3-(phenyl carbamoyl)-1-thioxo-4,5dihydro[1,3]thiazolo[3,4-a]quinazoline-8-carboxylate
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Kant S, et al. Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 11;7(1):5067.
molnova catalog



related products
-
1,3-DIMETHYL-2-OXO-2...
1,3-DIMETHYL-2-OXO-2,3-DIHYDRO-1H-BENZIMIDAZOLE-5-CARBALDEHYDE
-
Dup-721
DuP-721 is a broad spectrum and orally active antibacterial agent against a variety of clinically susceptible and resistant bacteria, especially M. tuberculosis.
-
Entospletinib
Entospletinib (IC50= 7.7 nM)is a specific Syk inhibitor, which is orally bioavailable.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


