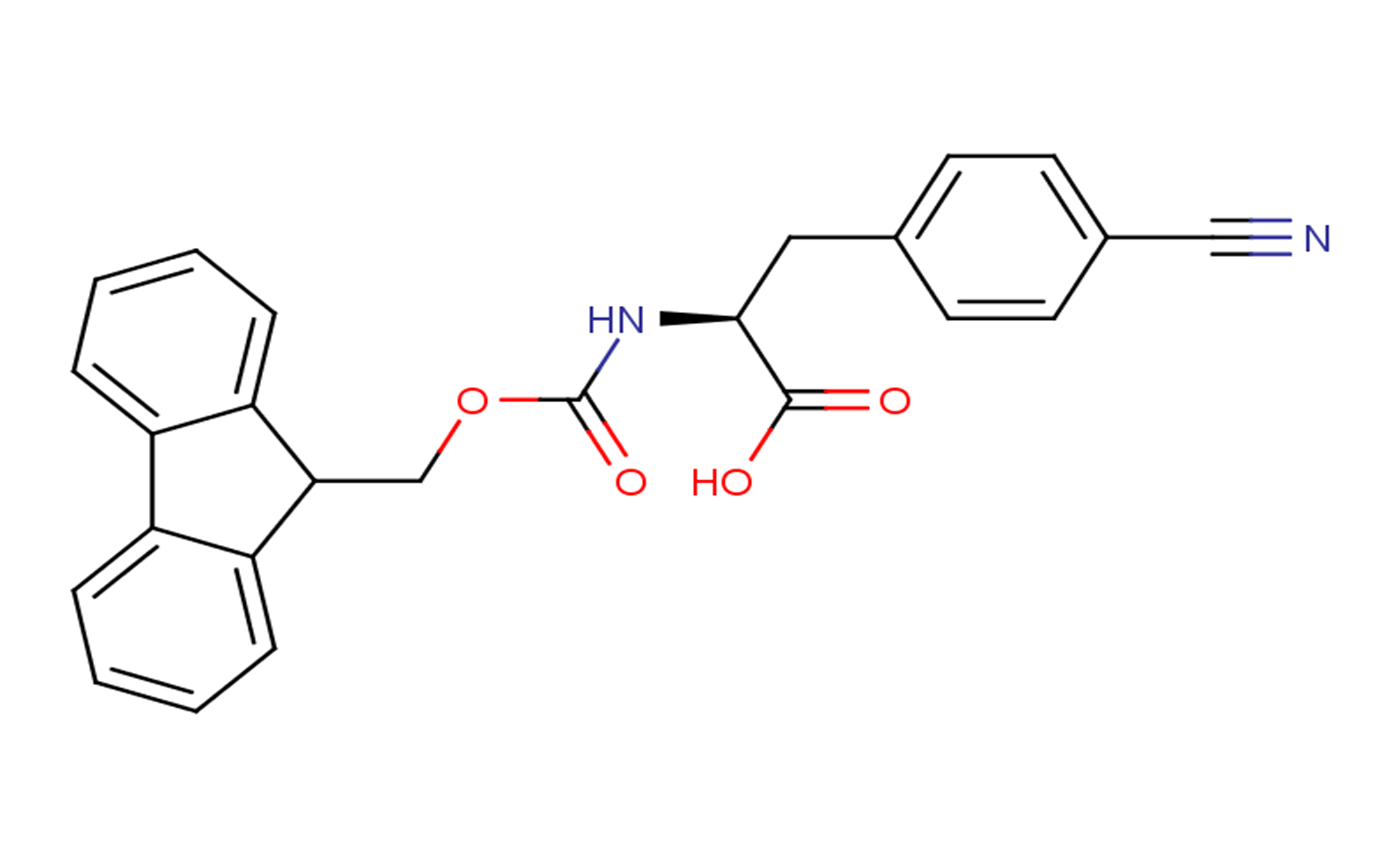
Fmoc-Phe(4-CN)-OH
CAS No. 173963-93-4
Fmoc-Phe(4-CN)-OH( FMOC-L-4-CYANOPHENYLALANINE )
Catalog No. M23785 CAS No. 173963-93-4
Fmoc-Phe(4-CN)-OH is an N-Fmoc protected phenylalanine derivative and potentially useful synthetic intermediate.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 37 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 87 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameFmoc-Phe(4-CN)-OH
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionFmoc-Phe(4-CN)-OH is an N-Fmoc protected phenylalanine derivative and potentially useful synthetic intermediate.
-
DescriptionFmoc-Phe(4-CN)-OH is an N-Fmoc protected phenylalanine derivative and potentially useful synthetic intermediate
-
In VitroAmino acids and amino acid derivatives have been commercially used as ergogenic supplements. They influence the secretion of anabolic hormones, supply of fuel during exercise, mental performance during stress related tasks and prevent exercise induced muscle damage. They are recognized to be beneficial as ergogenic dietary substances.
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsFMOC-L-4-CYANOPHENYLALANINE
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number173963-93-4
-
Formula Weight412.44
-
Molecular FormulaC25H20N2O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:10 mM
-
SMILESC1=CC=C2C(=C1)C(C3=CC=CC=C32)COC(=O)N[C@@H](CC4=CC=C(C=C4)C#N)C(=O)O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
RO5263397
RO5263397 is a TAAR1 specific agonist with oral activity that has been used in antidepressant studies.
-
Fendosal
Fendosal is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent. It is 6.9 to 9.5 times more active than aspirin in the prophylactic and therapeutic adjuvant-induced polyarthritis models of chronic inflammation.
-
Orsellinic acid ethy...
Orsellinic acid ethyl ester is a phenolic acid, extracted from lichens.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


