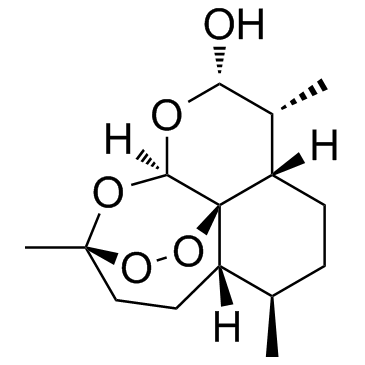
Dihydroartemisinin
CAS No. 71939-50-9
Dihydroartemisinin( DHQHS 2 | Dihydroqinghaosu )
Catalog No. M15752 CAS No. 71939-50-9
Dihydroartemisinin (DHA) is a semi-synthetic derivative of artemisinin and isolated from the traditional Chinese herb Artemisia annua.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 50MG | 61 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameDihydroartemisinin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionDihydroartemisinin (DHA) is a semi-synthetic derivative of artemisinin and isolated from the traditional Chinese herb Artemisia annua.
-
DescriptionDihydroartemisinin (DHA) is a semi-synthetic derivative of artemisinin and isolated from the traditional Chinese herb Artemisia annua.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsDHQHS 2 | Dihydroqinghaosu
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research AreaInfection
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number71939-50-9
-
Formula Weight284.35
-
Molecular FormulaC15H24O5
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityEthanol: 11 mg/mL warmed (38.68 mM); DMSO: 56 mg/mL warmed (196.94 mM)
-
SMILESO[C@@H]1[C@H](C)[C@]2([H])CC[C@@H](C)[C@]3([H])CC[C@@](O4)(C)OO[C@]32[C@]4([H])O1
-
Chemical Name(3R,5aS,6R,8aS,9R,10S,12R,12aR)-3,6,9-trimethyldecahydro-12H-3,12-epoxy[1,2]dioxepino[4,3-i]isochromen-10-ol
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Yang D, et al. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Feb 1;8(2):1270-8
molnova catalog



related products
-
Antiproliferative ag...
Antiproliferative agent-15 is a reagent with anticancer activity. Antiproliferative agent-15 showed antiproliferative activity against human colon cancer (HCT116 and HCT15) and brain cancer (LN-229 and GBM-10).
-
HIV-1 gag Protein p2...
HIV-1 gag Protein p24 (137-154)
-
Enprofylline
Enprofylline, a bronchodilator, acts primarily as a competitive nonselective phosphodiesterase inhibitor.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


