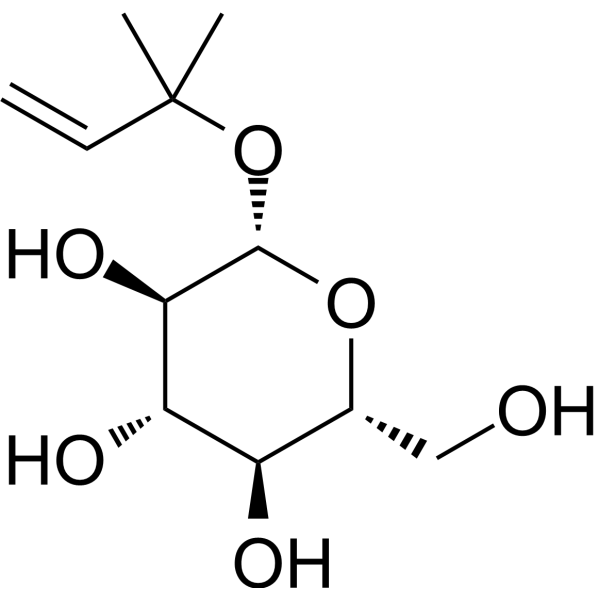
Crenulatin
CAS No. 63026-02-8
Crenulatin( —— )
Catalog No. M31600 CAS No. 63026-02-8
Crenulatin has dual- direction effects on apoptosis of cerebral microvascular endothelial cells, inhibitive effect in 25 mg/L and stimulative effect in 100 mg/L group, respectively; the mechanism is related to the alterations of Fas/Bcl-2 expression and caspase-3 activity.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 144 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCrenulatin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCrenulatin has dual- direction effects on apoptosis of cerebral microvascular endothelial cells, inhibitive effect in 25 mg/L and stimulative effect in 100 mg/L group, respectively; the mechanism is related to the alterations of Fas/Bcl-2 expression and caspase-3 activity.
-
DescriptionCrenulatin has dual- direction effects on apoptosis of cerebral microvascular endothelial cells, inhibitive effect in 25 mg/L and stimulative effect in 100 mg/L group, respectively; the mechanism is related to the alterations of Fas/Bcl-2 expression and caspase-3 activity.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number63026-02-8
-
Formula Weight248.27
-
Molecular FormulaC11H20O6
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILES——
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Glycochenodeoxycholi...
Glycolithocholic acid is a glycine conjugate of lithocholic acid, a bile acid. It is increased in livers of mice that are fed diets supplemented with ursadeoxycholic acid.
-
Emitefur
Emitefur (BOF-A 2) is an orally active and potent 5-fluorouracil derivative with anticancer and antitumor activity.
-
Pomalidomide-PEG4-C2...
Pomalidomide-PEG4-C2-NH2 hydrochloride is a PEG-based PROTAC linker that can be used to synthesize PROTACs.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


