Cerdulatinib
CAS No. 1198300-79-6
Cerdulatinib( PRT2070 | PRT-062070 | Cerdulatinib )
Catalog No. M17872 CAS No. 1198300-79-6
Cerdulatinib is an novel oral dual Syk/JAK inhibitor.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 45 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 65 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 97 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 176 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 286 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 492 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 633 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 972 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCerdulatinib
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCerdulatinib is an novel oral dual Syk/JAK inhibitor.
-
DescriptionCerdulatinib, also known as PRT2070 and PRT062070, is a n ovel, oral, dual spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) and janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor. Cerdulatinib preferentially inhibited JAK1 and JAK3 dependent cytokine mediated signaling and functional responses in various cell types. IL2 mediated STAT5 Y694 was inhibited with an IC50 of 0.27μM, while IL4 mediated signaling to STAT6 Y641 and functional responses in B cells and monocytes, namely CD69, CD25, and CD23 up-regulation, were inhibited with IC50 ’s within the range of 0.11μM to 0.57μM. It is currently being studied in patients with genetically-defined hematologic cancers, as well as for patients who have failed therapy due to relapse or acquired mutations.(In Vitro):Cerdulatinib shows inhibitory effect on 60 CLL with IC50 ranging from 0.37 to 10.02 μM. Cerdulatinib induces apoptosis in CLL in association with MCL-1 down-regulation and PARP cleavage. Cerdulatinib (2μM) is able to overcome the support of the microenvironment and induces CLL cell death. Cerdulatinib (250-500 nM) blocks proliferation of ibrutinib-sensitive and ibrutinib-resistant primary CLL cells. Cerdulatinib also blocks proliferation of both ibrutinib-sensitive and ibrutinib-resistant primary CLL cells as well as BTKC481S-transfected cell lines, and blocks BCR and JAK-STAT signaling pathways. Furthermore, inhibition of SYK and JAK by cerdulatinib translates to downstream inhibition of AKT and ERK. Cerdulatinib inhibits the activity of NF-kB pathway. PRT062070 reduces the ability of stimulated B cells to upregulate cell-surface expression of the early activation marker CD69 (IC50=0.11 μM). PRT062070 exhibits differential potency against cytokine JAK/STAT signaling pathways. PRT062070 (1 or 3 μM) induces apoptosis in BCR-signaling competent NHL cell lines. Cerdulatinib demonstrates inhibitory activity against both ABC and GCB subtypes of DLBCL cells. Cerdulatinib also induces apoptosis in both GCB and ABC subtypes of DLBCL cell lines via caspase 3 and PARP cleavage. And cerdulatinib blocks cell cycle in both ABC and GCB subtypes of DLBCL via inhibition of RB phosphorylation and down-regulation of cyclin E. Cerdulatinib induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis under the condition of BCR stimulation in all DLBCL cell lines. Besides, cerdulatinib blocks JAK/STAT and BCR signaling in both ABC and GCB DLBCL cell lines. Cerdulatinib induces cell death in primary human DLBCL samples. Cerdulatinib inhibits BCR-induced signals in a dose-dependent manner and most strongly between 0.3 to 1 μM. and particularly in IGHV-unmutated samples with greater BCR signaling capacity and response to IL4, or samples expressing higher levels of sIgM, CD49d+, or ZAP70+. Cerdulatinib overcomes anti-IgM, IL4/CD40L, or NLC-mediated protection by preventing upregulation of MCL-1 and BCL-XL; however, BCL-2 expression is unaffected. Furthermore, in samples treated with IL4/CD40L, cerdulatinib synergizes with venetoclax in vitro to induce greater apoptosis than either drug alone.(In Vivo):PRT062070 (0.5 mg/kg) results in a nonstatistically significant trend toward reduced ankle inflammation, whereas significant reductions in inflammation are achieved with the 1.5, 3, and 5 mg/kg doses. PRT062070 also affects anticollagen antibody formation. PRT062070 (15 mg/kg) suppresses upregulation of splenic B-cell surface CD80/86 and CD69, and inhibits BCR signaling and activation in the spleen after oral dosing in mice.
-
In VitroCerdulatinib shows inhibitory effect on 60 CLL with IC50 ranging from 0.37 to 10.02 μM. Cerdulatinib induces apoptosis in CLL in association with MCL-1 down-regulation and PARP cleavage. Cerdulatinib (2μM) is able to overcome the support of the microenvironment and induces CLL cell death. Cerdulatinib (250-500 nM) blocks proliferation of ibrutinib-sensitive and ibrutinib-resistant primary CLL cells. Cerdulatinib also blocks proliferation of both ibrutinib-sensitive and ibrutinib-resistant primary CLL cells as well as BTKC481S-transfected cell lines, and blocks BCR and JAK-STAT signaling pathways. Furthermore, inhibition of SYK and JAK by cerdulatinib translates to downstream inhibition of AKT and ERK. Cerdulatinib inhibits the activity of NF-kB pathway. PRT062070 reduces the ability of stimulated B cells to upregulate cell-surface expression of the early activation marker CD69 (IC50=0.11 μM). PRT062070 exhibits differential potency against cytokine JAK/STAT signaling pathways. PRT062070 (1 or 3 μM) induces apoptosis in BCR-signaling competent NHL cell lines. Cerdulatinib demonstrates inhibitory activity against both ABC and GCB subtypes of DLBCL cells. Cerdulatinib also induces apoptosis in both GCB and ABC subtypes of DLBCL cell lines via caspase 3 and PARP cleavage. And cerdulatinib blocks cell cycle in both ABC and GCB subtypes of DLBCL via inhibition of RB phosphorylation and down-regulation of cyclin E. Cerdulatinib induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis under the condition of BCR stimulation in all DLBCL cell lines. Besides, cerdulatinib blocks JAK/STAT and BCR signaling in both ABC and GCB DLBCL cell lines. Cerdulatinib induces cell death in primary human DLBCL samples. Cerdulatinib inhibits BCR-induced signals in a dose-dependent manner and most strongly between 0.3 to 1 μM. and particularly in IGHV-unmutated samples with greater BCR signaling capacity and response to IL4, or samples expressing higher levels of sIgM, CD49d+, or ZAP70+. Cerdulatinib overcomes anti-IgM, IL4/CD40L, or NLC-mediated protection by preventing upregulation of MCL-1 and BCL-XL; however, BCL-2 expression is unaffected. Furthermore, in samples treated with IL4/CD40L, cerdulatinib synergizes with venetoclax in vitro to induce greater apoptosis than either drug alone.
-
In VivoPRT062070 (0.5 mg/kg) results in a nonstatistically significant trend toward reduced ankle inflammation, whereas significant reductions in inflammation are achieved with the 1.5, 3, and 5 mg/kg doses. PRT062070 also affects anticollagen antibody formation. PRT062070 (15 mg/kg) suppresses upregulation of splenic B-cell surface CD80/86 and CD69, and inhibits BCR signaling and activation in the spleen after oral dosing in mice.
-
SynonymsPRT2070 | PRT-062070 | Cerdulatinib
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorJAK1| JAKs| Syk
-
Research AreaCancer
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1198300-79-6
-
Formula Weight445.54
-
Molecular FormulaC20H27N7O3S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO : ≥ 30 mg/mL; 67.33 mM
-
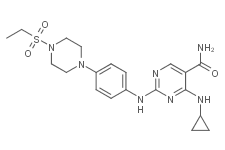
SMILESCCS(=O)(=O)N1CCN(CC1)c1ccc(cc1)Nc1ncc(C(=O)N)c(NC2CC2)n1
-
Chemical Name4-(cyclopropylamino)-2-((4-(4-(ethylsulfonyl)piperazin-1-yl)phenyl)amino)pyrimidine-5-carboxamide
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Coffey G, et al. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014 Dec;351(3):538-48.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Pyridoxal hydrochlor...
The 4-carboxyaldehyde form of vitamin B6 which is converted to pyridoxal phosphate which is a coenzyme for synthesis of amino acids neurotransmitters (serotonin norepinephrine) sphingolipids aminolevulinic acid.
-
4-Hydroxybenzyl alco...
4-Hydroxybenzyl alcohol exhibits beneficial effects in cerebral ischemic injury, has neuroprotective effect through upregulation of Nrf2, Prdx6, and PDI expression via the PI3K/Akt pathway.
-
OGG1-IN-O8
OGG1-IN-O8 is an inhibitor of 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase 1 (OGG1;IC50 : 0.35 μM).



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


