Canthaxanthin
CAS No. 514-78-3
Canthaxanthin( E 161g | all-trans-Canthaxanthin )
Catalog No. M24483 CAS No. 514-78-3
Canthaxanthin is a red-orange carotenoid that belongs to the xanthophyll group.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 57 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 87 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 141 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 257 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 429 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 617 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 1332 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCanthaxanthin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCanthaxanthin is a red-orange carotenoid that belongs to the xanthophyll group.
-
DescriptionCanthaxanthin is a red-orange carotenoid that belongs to the xanthophyll group. This naturally occurring pigment is present in bacteria, algae and some fungi.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsE 161g | all-trans-Canthaxanthin
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number514-78-3
-
Formula Weight564.84
-
Molecular FormulaC40H52O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
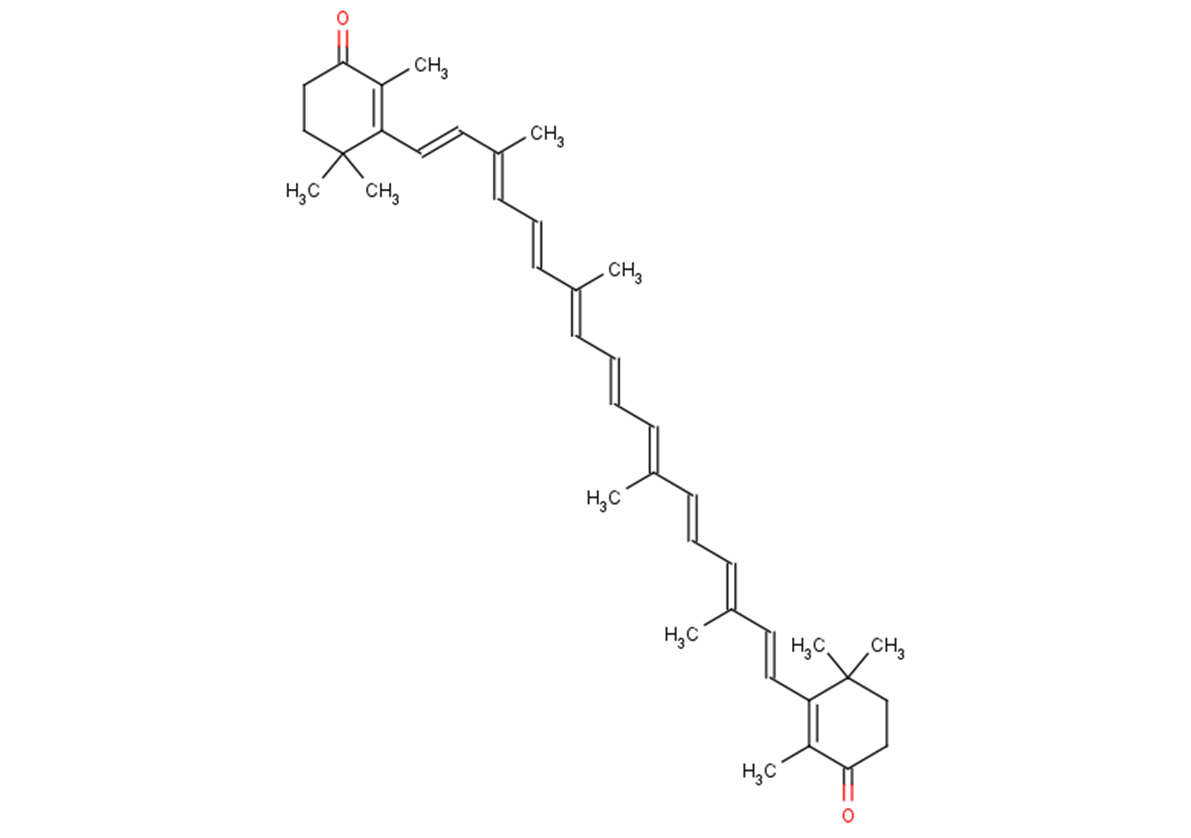
SMILESCC(C)(CC1)C(/C=C/C(/C)=C/C=C/C(/C)=C/C=C/C=C(\C)/C=C/C=C(\C)/C=C/C(C(C)(C)CC2)=C(C)C2=O)=C(C)C1=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Tuba, Esatbeyoglu, Gerald, et al. Canthaxanthin: From molecule to function[J]. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research, 2017.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Phenoxyethanol
Phenoxyethanol is germicidal. It often used together with quaternary ammonium compounds.
-
Esonarimod
Esonarimod is an antirheumatic drug.
-
DIM-C-pPhCO2Me
DIM-C-pPhCO2Me is a nuclear receptor 4A1 (NR4A1) antagonist.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


