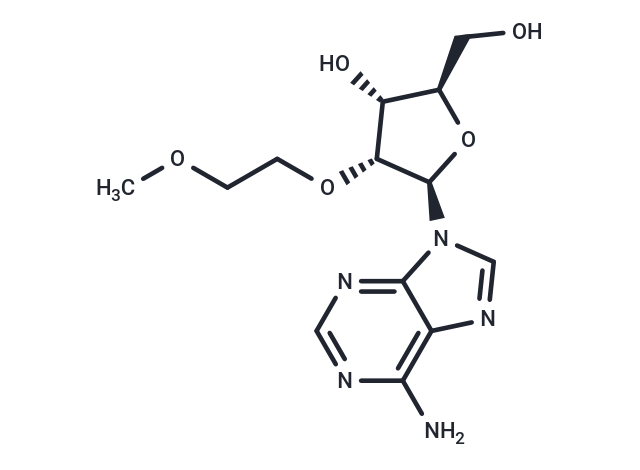
2-O-(2-Methoxyethyl)adenosine
CAS No. 168427-74-5
2-O-(2-Methoxyethyl)adenosine( —— )
Catalog No. M37874 CAS No. 168427-74-5
2'-O-(2-Methoxyethyl)adenosine is a nucleoside analog used to improve RNA target affinity and nuclease resistance of therapeutic oligonucleotides in preclin.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 50MG | 28 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 38 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | 97 | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | 146 | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name2-O-(2-Methoxyethyl)adenosine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description2'-O-(2-Methoxyethyl)adenosine is a nucleoside analog used to improve RNA target affinity and nuclease resistance of therapeutic oligonucleotides in preclin.
-
Description2′-O-(2-Methoxyethyl)adenosine is a compound can be used in the synthesis of oligonucleotides.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayCell Cycle/DNA Damage
-
TargetDNA/RNA Synthesis
-
RecptorDNA/RNA Synthesis
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number168427-74-5
-
Formula Weight325.32
-
Molecular FormulaC13H19N5O5
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 50 mg/mL (153.69 mM; Ultrasonic )
-
SMILESCOCCO[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H]1N1C=NC2=C(N)N=CN=C12
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Marais G, et al. Chemo-enzymatic synthesis of 2'-O-methoxyethyl ribonucleosides using a phosphodiesterase from Serratia marcescens. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2005;66(5):512-519.?
molnova catalog



related products
-
PNR-7-02
PNR-7-02 is a specific inhibitor of human DNA Polymerase η (hPol η) with IC50 of 8 uM.
-
DNA polymerase-IN-1
DNA polymerase-IN-1, a DNA polymerase inhibitor, exhibited antiproliferative activity against tumor cells with a half-inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 20.7 μM.
-
Deoxythymidine triph...
Deoxythymidine triphosphate (dTTP) is one of the four nucleoside triphosphates that are used in the in vivo synthesis of DNA.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


