DNA polymerase-IN-1
CAS No. 809234-33-1
DNA polymerase-IN-1( —— )
Catalog No. M37273 CAS No. 809234-33-1
DNA polymerase-IN-1, a DNA polymerase inhibitor, exhibited antiproliferative activity against tumor cells with a half-inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 20.7 μM.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 459 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 657 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 1026 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 1386 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 1832 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameDNA polymerase-IN-1
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionDNA polymerase-IN-1, a DNA polymerase inhibitor, exhibited antiproliferative activity against tumor cells with a half-inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 20.7 μM.
-
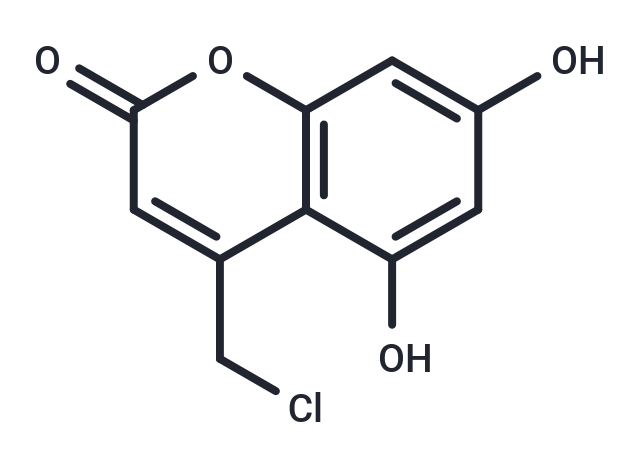
DescriptionDNA polymerase-IN-1 (compound 2d) is a DNA polymerase inhibitor (IC50=20.7 μM) with antiproliferative activity against tumor cells.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayCell Cycle/DNA Damage
-
TargetDNA/RNA Synthesis
-
RecptorDNA/RNA Synthesis | Antiviral
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number809234-33-1
-
Formula Weight226.61
-
Molecular FormulaC10H7ClO4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESO=C1OC=2C=C(O)C=C(O)C2C(=C1)CCl
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Bruna-Haupt EF, et al. Synthesis of Structurally Related Coumarin Derivatives as Antiproliferative Agents. ACS Omega. 2023 Jul 13;8(29):26479-26496.?
molnova catalog



related products
-
Tallimustine HCl
Tallimustine HCl is a DNA inhibitor, an AT-specific alkylated antitumor derivative of diamycin.Tallimustine HCl can be used in severe combined immunodeficiency mouse models of adult myelogenous leukemia, which can be used for the treatment of leukemia.
-
Mithramycin A
A tricyclic pentaglycosidic, antineoplastic antibiotic from Streptomyces strains that inhibits RNA and protein synthesis by adhering to DNA.
-
Apricitabine
Apricitabine (SPD754) is a highly selective and orally active HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitor (Ki=0.08 μM), the (-) enantiomer of 2′-deoxy-3′-oxy-4′-thiocytidine (dOTC) .



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


