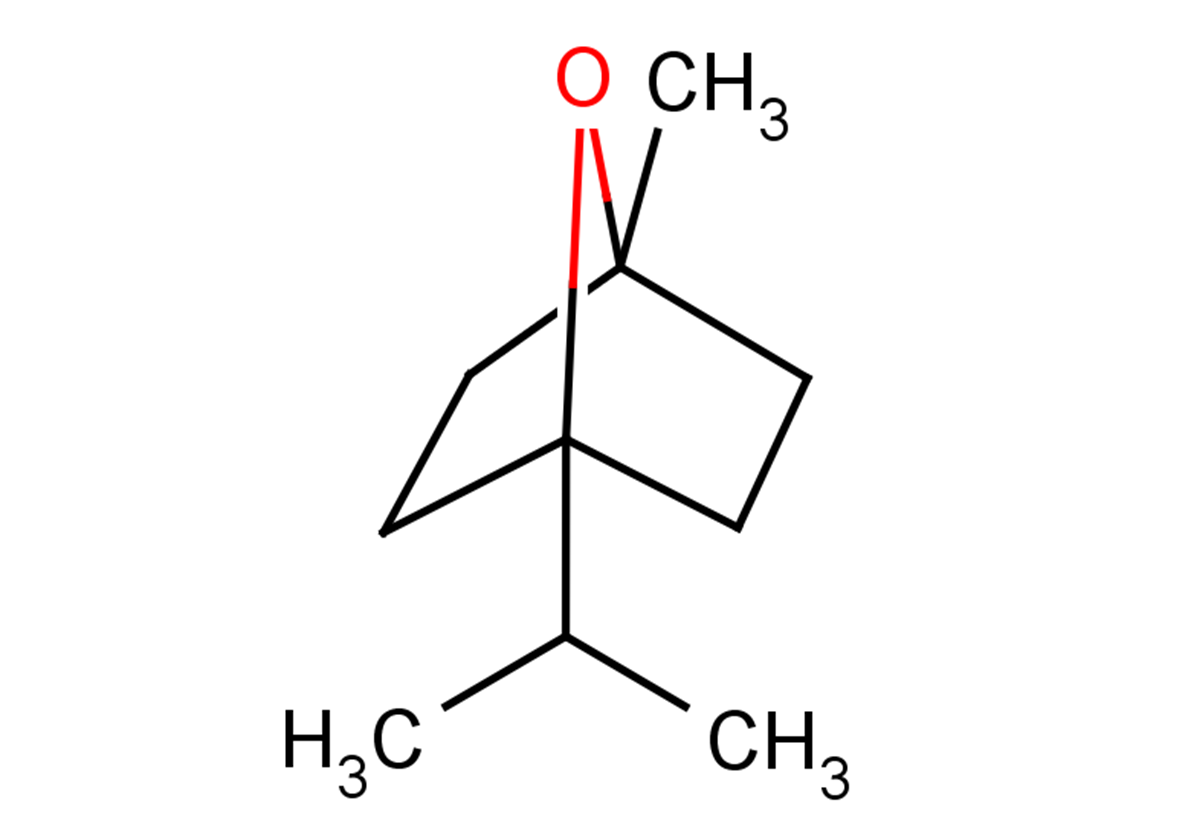
1,4-Cineole
CAS No. 470-67-7
1,4-Cineole( Isocineole )
Catalog No. M24419 CAS No. 470-67-7
1,4-Cineole is a natural, oxygenated monoterpene. 1,4-Cineole can activate both human TRPM8 and human TRPA1.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 37 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name1,4-Cineole
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description1,4-Cineole is a natural, oxygenated monoterpene. 1,4-Cineole can activate both human TRPM8 and human TRPA1.
-
Description1,4-Cineole is a natural, oxygenated monoterpene. 1,4-Cineole can activate both human TRPM8 and human TRPA1.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsIsocineole
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorEndogenous Metabolite|TRPA1|TRPM8
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number470-67-7
-
Formula Weight154.25
-
Molecular FormulaC10H18O
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO : 125 mg/mL (810.37 mM; Need ultrasonic)
-
SMILESCC(C12CCC(O2)(C)CC1)C
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Takaishi M, et al. 1,8-cineole, a TRPM8 agonist, is a novel natural antagonist of human TRPA1. Mol Pain. 2012 Nov 29;8:86.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Alloepipregnanolone
Alloepipregnanolone is a pregnane with anesthetic hypnotic and sedative properties.
-
5a-Pregnane-320-dion...
5a-Pregnane-320-dione is a biologically active 5-alpha-reduced metabolite of plasma progesterone
-
Dimethyl sulfone
Dimethyl sulfone exists in all living organisms, ranging from bacteria to humans.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


