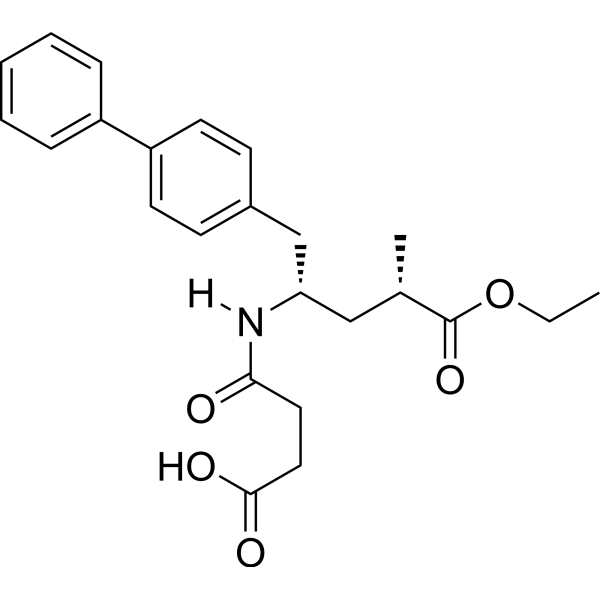
(2S,4S)-Sacubitril
CAS No. 149709-63-7
(2S,4S)-Sacubitril( Sacubitril Impurity C )
Catalog No. M27052 CAS No. 149709-63-7
(2S,4S)-Sacubitril is a stereoisomer derived from Sacubitril which is a potent NEP inhibitor.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 448 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 683 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 1161 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 1764 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 2673 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name(2S,4S)-Sacubitril
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description(2S,4S)-Sacubitril is a stereoisomer derived from Sacubitril which is a potent NEP inhibitor.
-
Description(2S,4S)-Sacubitril is a stereoisomer derived from Sacubitril which is a potent NEP inhibitor.
-
In Vitro(2S,4S)-Sacubitril is a stereoisomer derived from Sacubitril.
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsSacubitril Impurity C
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorSARS-CoV-2 3CL
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number149709-63-7
-
Formula Weight430.49
-
Molecular FormulaC24H28NO5 1/2Ca
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESO=C([O-])CCC(N[C@@H](C[C@H](C)C(OCC)=O)CC1=CC=C(C2=CC=CC=C2)C=C1)=O.O=C([O-])CCC(N[C@@H](C[C@H](C)C(OCC)=O)CC3=CC=C(C4=CC=CC=C4)C=C3)=O.[Ca+2]
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Yuto Unoh, et al. Discovery of S-217622, a Non-Covalent Oral SARS-CoV-2 3CL Protease Inhibitor Clinical Candidate for Treating COVID-19. bioRxiv 2022.01.26.477782.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Glycerophosphocholin...
Glycerylphosphorylcholine is a natural choline compound found in the brain and in milk. It is also a parasympathomimetic acetylcholine precursor which may have a potential for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and dementia.
-
Depressine
Depressine is a natural product from Gentiana depressa.
-
Bis(2-methyl-3-furyl...
Bis(2-Methyl-3-furyl) disulfide is a volatile sulfur compound that is a key contributor to the meat-like aroma in cooked meat.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


