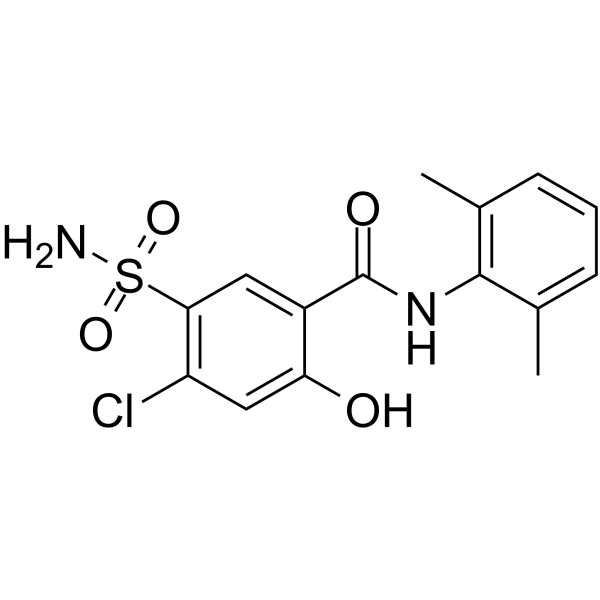
Xipamide
CAS No. 14293-44-8
Xipamide( Diurexan | Aquaphor )
Catalog No. M26867 CAS No. 14293-44-8
Xipamide is a sulfonamide-based diuretic with antihypertensive properties. Xipamide selectively inhibits anion exchanger.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 10MG | 39 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 80 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 151 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 224 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | 331 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameXipamide
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionXipamide is a sulfonamide-based diuretic with antihypertensive properties. Xipamide selectively inhibits anion exchanger.
-
DescriptionXipamide is a sulfonamide-based diuretic with antihypertensive properties. Xipamide selectively inhibits anion exchanger.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsDiurexan | Aquaphor
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorCB1| GABAB
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number14293-44-8
-
Formula Weight354.81
-
Molecular FormulaC15H15ClN2O4S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 250 mg/mL (704.60 mM)
-
SMILESCc1cccc(C)c1NC(=O)c1cc(c(Cl)cc1O)S(N)(=O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Francesca Ferlenghi, et al. The GABA B receptor positive allosteric modulator COR659: In vitro metabolism, in vivo pharmacokinetics in rats, synthesis and pharmacological characterization of metabolically protected derivatives. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2020 Dec 1;155:105544.
molnova catalog



related products
-
19 alpha-Hydroxyasia...
19 alpha-Hydroxyasiatic acid shows significant anticoagulant effect on the extrinsic pathway.
-
T3Inh-1
T3Inh-1 is an effective and selective inhibitor of ppGalNAc-T3 with an IC50 of 7 μM. T3Inh-1 prevents breast cancer cells. T3Inh-1 reduces FGF23 hormone levels in both tissue cells and mice, without causing any toxic side effects.
-
Volvalerenic acid A
Volvalerenic acid A is a natural product.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


