Vidofludimus
CAS No. 717824-30-1
Vidofludimus( Vidofludimus | 4SC 101 | 4SC101 | SC12267 )
Catalog No. M17579 CAS No. 717824-30-1
Vidofludimus (4SC-101, SC12267) is a novel small molecule inhibitor of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 49 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 69 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 113 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 207 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 332 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 470 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameVidofludimus
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionVidofludimus (4SC-101, SC12267) is a novel small molecule inhibitor of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH).
-
DescriptionVidofludimus, also known as 4SC 101 or SC12267, is a novel orally active and potent DHODH inhibitor. In vitro, 4SC-101 is a potent inhibitor of human DHODH, inhibits lymphocyte proliferation, and uniquely blocks phytohemagglutinin-stimulated IL-17 production by lymphocytes. In vivo, oral administration of 4SC-101 effectively improved both chronic DSS and acute TNBS colitis in mice. 4SC-101 may have potential for the treatment of intestinal inflammation. Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) is a key enzyme involved in pyrimidine biosynthesis. DHODH is a known target for the treatment of autoimmune diseases.(In Vitro):Vidofludimus (0-1 μM) selectively activats FXR in a concentration dependent manner with an EC50 value of about 450 nM in inducing the recruitment of various coactivator LXXLL motifs.Vidofludimus (0-8 μM) blocks nuclear translocation of p65 by suppressing IKK-IκB-NF-κB pathway.Vidofludimus has inhibitory activity for human DHODH with an IC50 value of 160 nM.Vidofludimus inhibits dihydro-orotate dehydrogenase and lymphocyte proliferation in vitro.Vidofludimus inhibits interleukin (IL)-17 secretion in vitro independently of effects on lymphocyte proliferation.Vidofludimus completely blocks IL-23 + IL-1β-stimulated secretion of IL-17 by colonic strips in ex vivo.(In Vivo):Vidofludimus (i.p.; once daily; for 14 days) exerts effects on dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) induced colitis in an FXR-dependent manner in vivo.Vidofludimus (p.o; 60 mg/kg; for 6 days) effectively improves many parameters of TNBS-induced colitis in rats and has inhibitory effects on colonic STAT3 and IL-17.
-
In VitroVidofludimus (0-1 μM) selectively activats FXR in a concentration dependent manner with an EC50 value of about 450 nM in inducing the recruitment of various coactivator LXXLL motifs.Vidofludimus (0-8 μM) blocks nuclear translocation of p65 by suppressing IKK-IκB-NF-κB pathway.Vidofludimus has inhibitory activity for human DHODH with an IC50 value of 160 nM.Vidofludimus inhibits dihydro-orotate dehydrogenase and lymphocyte proliferation in vitro.Vidofludimus inhibits interleukin (IL)-17 secretion in vitro independently of effects on lymphocyte proliferation.Vidofludimus completely blocks IL-23 + IL-1β-stimulated secretion of IL-17 by colonic strips in ex vivo. Western Blot Analysis Cell Line:HepG2 cells or MEFs Concentration:2, 8 μM Incubation Time:1 h Result:Inhibited of TNFα-induced IKKα/β phosphorylation and IκBα degradation.RT-PCRCell Line:HepG2 cells Concentration:5 μM Incubation Time:24 h Result:Inhibited the increase of NF-κB target genes MCP-1 and CXCL-2 upon TNFα stimulation.
-
In VivoVidofludimus (i.p.; once daily; for 14 days) exerts effects on dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) induced colitis in an FXR-dependent manner in vivo.Vidofludimus (p.o; 60 mg/kg; for 6 days) effectively improves many parameters of TNBS-induced colitis in rats and has inhibitory effects on colonic STAT3 and IL-17. Animal Model:homozygous FXR deficient (FXR KO) mice(10-week-old, male)Dosage:20 mg/kg Administration:oral, 20 mg/kg/day Result: Revealed multifocal inflammatory cell infiltration and edema with crypt and epithelial cell destruction and ulceration.Animal Model:NAFLD Model(10-11 weeks old male obese Lepob/ob C57BL/6 (ob/ob) mice)Dosage:10 mg/kg Administration:intraperitoneally, once daily, for 14 days Result:Significantly reduced body weight loss, prevented colonic shortening, decreased histological scores, and disease activity index (DAI) scores in WT mice.Significantly decreased colonic mRNA expression of the pro-inflammatorygenes interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, IL-17, and prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (COX-2).Animal Model:Wistar ratsDosage:60 mg/kg Administration:p.o., for 6 days Result:Effectively reduced macroscopic and histological pathology and the numbers of CD3+ T cells in vivo.Reduced nuclear signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) binding and IL-17 levels.
-
SynonymsVidofludimus | 4SC 101 | 4SC101 | SC12267
-
PathwayEndocrinology/Hormones
-
Target5-HT Receptor
-
RecptorHuman DHODH
-
Research AreaInflammation/Immunology
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number717824-30-1
-
Formula Weight355.36
-
Molecular FormulaC20H18FNO4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO : ≥ 46 mg/mL; 129.45 mM
-
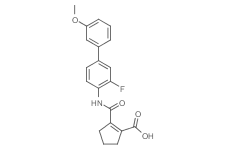
SMILESCOc1cccc(c1)c1cc(F)c(NC(=O)C2=C(CCC2)C(=O)O)cc1
-
Chemical Name2-((3-fluoro-3'-methoxy-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)carbamoyl)cyclopent-1-enecarboxylic acid
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Kulkarni OP, et al. Am J Pathol. 2010 Jun;176(6):2840-7.
molnova catalog



related products
-
3-AQC
3-AQC is a competitive antagonist of 5-HT3.
-
Prucalopride
Prucalopride is a selective, high affinity 5-HT receptor agonist for 5-HT4A and 5-HT4B receptor with Ki of 2.5 nM and 8 nM, respectively.
-
Dehydroaripiprazole
Dehydroaripiprazole is the active metabolite of aripiprazole. Aripiprazole is an antipsychotic drug, which is metabolized by CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 and mainly forms dehydroaripiprazole.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


