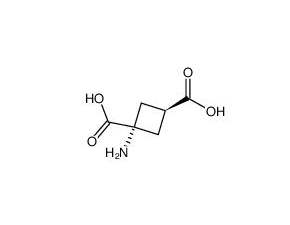
Trans-ACBD
CAS No. 117488-23-0
Trans-ACBD( trans-1-Aminocyclobutane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid | trans ABCD )
Catalog No. M17168 CAS No. 117488-23-0
1-Aminocyclobutane-1, 3-dicarboxylic acid is an effective and specific N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor agonist.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 43 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 59 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 88 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 207 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 360 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 536 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameTrans-ACBD
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description1-Aminocyclobutane-1, 3-dicarboxylic acid is an effective and specific N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor agonist.
-
DescriptionTrans-ABCD is a potent and selective NMDA agonist.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonymstrans-1-Aminocyclobutane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid | trans ABCD
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptoraspartate
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number117488-23-0
-
Formula Weight159.14
-
Molecular FormulaC6H9NO4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESC1[C@@H](C[C@@]1(C(=O)O)N)C(=O)O
-
Chemical Name(1r,3r)-1-Aminocyclobutane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Thomas HL, et al. cis-2,4-methanoglutamate is a potent and selective N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor agonist. 1990, 182(3):397-404
molnova catalog



related products
-
Linzagolix choline
Linzagolix choline is an orally available non-peptide gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonist. It can be used to study pain associated with uterine fibroids and endometriosis.
-
Protoporphyrin IX
Protoporphyrin IX, in the metabolism of porphyrin, is created by the enzyme protoporphyrinogen oxidase.
-
1-(2-Hydroxyethyl)im...
Used as pharmaceutical intermediates.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


