TP-472
CAS No. 2079895-62-6
TP-472 ( TP472 )
Catalog No. M13237 CAS No. 2079895-62-6
TP-472 is a novel BRD9/7 chemical probe that has excellent potency (BRD9 KD=33nM; BRD7 KD=340 nM by ITC).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameTP-472
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionTP-472 is a novel BRD9/7 chemical probe that has excellent potency (BRD9 KD=33nM; BRD7 KD=340 nM by ITC).
-
DescriptionTP-472 is a novel BRD9/7 chemical probe that has excellent potency (BRD9 KD=33nM; BRD7 KD=340 nM by ITC), >30 fold selectivity over all other bromodomain family members except BRD7 and is cell active (EC50 320 nM in a BRD9 NanoBRET assay); has a good PK profile and is suitable for in vivo applications.
-
SynonymsTP472
-
PathwayChromatin/Epigenetic
-
TargetBromodomain
-
RecptorBromodomain
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2079895-62-6
-
Formula Weight333.39
-
Molecular FormulaC20H19N3O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
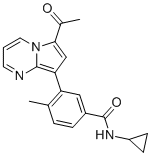
SMILESCC1=C(C=C(C=C1)C(=O)NC2CC2)C3=C4N=CC=CN4C(=C3)C(=O)C
-
Chemical Name3-(6-acetylpyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrimidin-8-yl)-N-cyclopropyl-4-methylbenzamide
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Pérez-Salvia M, et al. Epigenetics. 2017 May 4;12(5):323-339.
molnova catalog


related products
-
CPI703
A potent, selective, cell-active CBP/EP300 bromodomain inhibitor with IC50 of 0.47 uM for CBP.
-
I-BET151
I-BET151 (GSK1210151A) is a potent, selective BET bromodomain inhibitor.
-
ARV-825
ARV-825 is a hetero-bifunctional PROTAC (Proteolysis Targeting Chimera) that recruits BRD4 to the E3 ubiquitin ligase cereblon, leading to fast, efficient, and prolonged degradation of BRD4 via the proteasome.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


