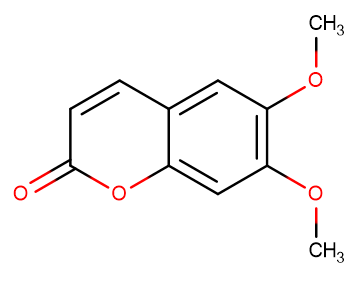
Scoparone
CAS No. 120-08-1
Scoparone( Aesculetin dimethyl ether | 6,7-Dimethoxycoumarin | 6,7-Dimethylesculetin | Escoparone )
Catalog No. M10722 CAS No. 120-08-1
Extracted from A.scoparia Waldst.e Kit seeds;Store the product in sealed, cool and dry condition.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 39 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 61 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 96 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 137 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 177 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | 230 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameScoparone
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionExtracted from A.scoparia Waldst.e Kit seeds;Store the product in sealed, cool and dry condition.
-
DescriptionExtracted from A.scoparia Waldst.e Kit seeds;Store the product in sealed, cool and dry condition.(In Vitro):Scoparone (0-0.4 nM; 24-48 hours) produces the most inhibition on PSC proliferation at 0.4 nM.(In Vivo):Scoparone (oral administration; 30 mg/kg, 60 mg/kg; 4 weeks) greatly ameliorates the pancreatic weight loss induced by DBTC in pancreatitis rats.
-
In VitroScoparone (0-0.4 nM; 24-48 hours) produces the most inhibition on PSC proliferation at 0.4 nM.
-
In VivoScoparone (oral administration; 30 mg/kg, 60 mg/kg; 4 weeks) greatly ameliorates the pancreatic weight loss induced by DBTC in pancreatitis rats. Animal Model:Chronic Pancreatitis (CP) Rat Models Dosage:30 mg/kg, 60 mg/kg Administration:Oral administration; 30 mg/kg, 60 mg/kg; 4 weeks Result:Protected against pancreatic damage.
-
SynonymsAesculetin dimethyl ether | 6,7-Dimethoxycoumarin | 6,7-Dimethylesculetin | Escoparone
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research AreaOther Indications
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number120-08-1
-
Formula Weight206.2
-
Molecular FormulaC11H10O4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: 10 mM
-
SMILESO=C1C=CC2=CC(OC)=C(OC)C=C2O1
-
Chemical Name6,7-Dimethoxy-2-benzopyrone
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Lee SH, Jang HD. Exp Cell Res. 2015 Feb 15;331(2):267-77.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Nonan-2-yl acetate
Nonan-2-yl acetate (Aceticacid2-nonylester) is a volatile oil extracted from the aerial parts of Ruta chalepensis L. and a pheromone extracted from honey bees with potential insecticidal activity.
-
Teriflunomide(b)
Teriflunomide is the principal active metabolite of leflunomide?an approved therapy for rheumatoid arthritis and?multiple sclerosis.
-
Ecabet Sodium
Ecabet sodium: a potential new agent in the management of distal colitis.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


