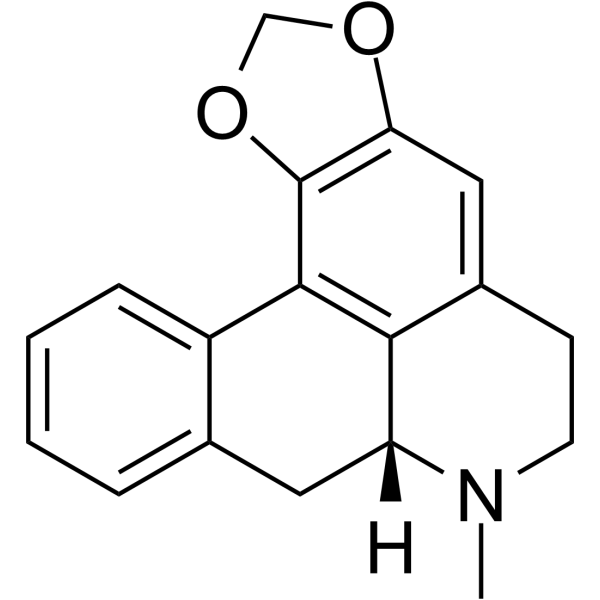
Roemerine
CAS No. 548-08-3
Roemerine( —— )
Catalog No. M31725 CAS No. 548-08-3
Roemerine is a potential active xanthine oxidase(XOD) inhibitor, XOD is a key enzyme in the pathogenesis of hyperuricemia and also a well-known target for the drug development to treat gout.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 508 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameRoemerine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionRoemerine is a potential active xanthine oxidase(XOD) inhibitor, XOD is a key enzyme in the pathogenesis of hyperuricemia and also a well-known target for the drug development to treat gout.
-
DescriptionRoemerine is a potential active xanthine oxidase(XOD) inhibitor, XOD is a key enzyme in the pathogenesis of hyperuricemia and also a well-known target for the drug development to treat gout.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number548-08-3
-
Formula Weight279.33
-
Molecular FormulaC18H17NO2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (358.00 mM)
-
SMILES——
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference



-
Dermorphin Analog
Dermorphin Analog is an analog of Dermorphin. Dermorphin is a natural heptapeptide μ-opioid receptor agonist found in amphibian skin. The dermorphin-derived peptide [Dmt1] dermorphin analog labels m-opioid receptors with high affinity and selectivity in receptor binding assays.
-
SXC 2023
SXC 2023 ((S)-2-acetamido-3-(4-methylbenzoylthio)propanoic acid) is a therapeutic prodrug of N-acetyl-L-cysteine for the treatment of CNS disorders and neurocognitive disorders, and can be used to treat glutamatergic dysfunction and psychiatric disorders in which oxidative stress plays a key role.
-
Cucurbitacin Q1
Cucurbitacin Q1 is identified as the fruit of Cucumis prophetarum and has been shown to be the pure trans component of cucurbitacin Q.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


