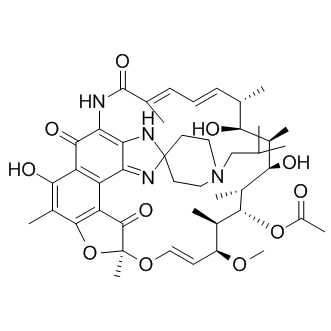
Rifabutin
CAS No. 72559-06-9
Rifabutin( Ansamycin | LM-427 )
Catalog No. M15779 CAS No. 72559-06-9
A semisynthetic ansamycin antibiotic with potent antimycobacterial properties.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 25MG | 38 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 50 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 71 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 127 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 214 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameRifabutin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionA semisynthetic ansamycin antibiotic with potent antimycobacterial properties.
-
DescriptionA semisynthetic ansamycin antibiotic with potent antimycobacterial properties. Bacterial Infection Approved(In Vitro):Rifabutin is primarily bactericidal antibiotic drug used to treat tuberculosis. Its effect on bacteria is based on the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase blocking drug rifamycin S., a semi-synthetic derivative. It is effective, for example, in highly resistant mycobacteria, Gram-positive bacteria (and some are effective against Gram-negative bacteria), but also against Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M. leprae, and M. avium intracellulare. Rifabutin is an antibiotic; antitumor. Rifabutin interferes with HSP-90 molecular chaperone, enhances ubiquitination and protein degradation, and inactivates bacterial RNA polymerase.
-
In VitroRifabutin is primarily bactericidal antibiotic drug used to treat tuberculosis. Its effect on bacteria is based on the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase blocking drug rifamycin S., a semi-synthetic derivative. It is effective, for example, in highly resistant mycobacteria, Gram-positive bacteria (and some are effective against Gram-negative bacteria), but also against Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M. leprae, and M. avium intracellulare. Rifabutin is an antibiotic; antitumor. Rifabutin interferes with HSP-90 molecular chaperone, enhances ubiquitination and protein degradation, and inactivates bacterial RNA polymerase.
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsAnsamycin | LM-427
-
PathwayGPCR/G Protein
-
TargetAntibacterial
-
RecptorEndoplasmin|HSP90|RNApolymerase
-
Research AreaInfection
-
IndicationBacterial Infection
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number72559-06-9
-
Formula Weight847.0047
-
Molecular FormulaC46H62N4O11
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility10 mM in DMSO
-
SMILESO=C1c2c(O)c(C)c3c(C4=O)c2C5=NC6(CCN(CC(C)C)CC6)NC5=C1NC(/C(C)=C/C=C/[C@@H]([C@H](O)[C@H]([C@@H](O)[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](C)[C@@H](OC)/C=C/O[C@]4(O3)C)OC(C)=O)C)C)C)=O
-
Chemical NameSpiro[9,4-(epoxypentadeca[1,11,13]trienimino)-2H-furo[2',3':7,8]naphth[1,2-d]imidazole-2,4'-piperidine]-5,10,26(3H,9H)-trione, 16-(acetyloxy)-6,18,20-trihydroxy-14-methoxy-7,9,15,17,19,21,25-heptamethyl-1'-(2-methylpropyl)-, (9S,12E,14S,15R,16S,17R,18R,19
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Cefoperazone sodium
Cefoperazone sodium salt is a cephalosporin antibiotic for inhibition of rMrp2-mediated [3H]E217βG uptake with IC50 of 199 μM.
-
Dalbavancin
Dalbavancin(MDL-63397, BI-397) is a novel second-generation lipoglycopeptide antibiotic that exerts its bactericidal effect by disrupting cell wall biosynthesis.
-
Ampicillin
Ampicillin is an orally active broad-spectrum antibiotic.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


