Dalbavancin
CAS No. 171500-79-1
Dalbavancin( MDL-63397 | BI-397 )
Catalog No. M12613 CAS No. 171500-79-1
Dalbavancin(MDL-63397, BI-397) is a novel second-generation lipoglycopeptide antibiotic that exerts its bactericidal effect by disrupting cell wall biosynthesis.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 116 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 176 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 354 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 532 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 759 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameDalbavancin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionDalbavancin(MDL-63397, BI-397) is a novel second-generation lipoglycopeptide antibiotic that exerts its bactericidal effect by disrupting cell wall biosynthesis.
-
DescriptionDalbavancin(MDL-63397, BI-397) is a novel second-generation lipoglycopeptide antibiotic that exerts its bactericidal effect by disrupting cell wall biosynthesis.
-
In VitroDalbavancin is a parenterally administered semisynthetic lipoglycopeptide developed to combat infections caused by resistant gram-positive pathogens. Dalbavancin exhibits potent in vitro bactericidal activity against gram-positive pathogens including S. aureus (MRSA), VISA, and non-VanA strains of VRE. Dalbavancin is developed for the treatment of complicated skin and skin structure infections (cSSSIs), predominantly those caused by MRSA and β-hemolytic streptococci, organisms against which it has shown greater potency than existing glycopeptide therapeutic agents.
-
In VivoDalbavancin (15-240 mg/kg; intraperitoneal injection; every 36 h or 72 h; for 14 days; female BALB/c mice) treatment has a survival rate of 80% to 100% of mice with all dose regimens. Animal Model:Female BALB/c mice (6-8 weeks) challenged with Ames strain of B. anthracis Dosage:15 mg/kg, 30 mg/kg, 60 mg/kg, 120 mg/kg, 240 mg/kg Administration:Intraperitoneal injection; every 36 h or 72 h; for 14 days Result:The efficacy was 80 to 100%, as determined by the rate of survival at 42 days, when treatment was initiated 24 h postchallenge with regimens of 15 to 120 mg/kg every 36 h or 30 to 240 mg/kg every 72 h.
-
SynonymsMDL-63397 | BI-397
-
PathwayGPCR/G Protein
-
TargetAntibacterial
-
RecptorAntibacterial
-
Research AreaInfection
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number171500-79-1
-
Formula Weight1816.692
-
Molecular FormulaC88H100Cl2N10O28
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: ≥ 24 mg/mL
-
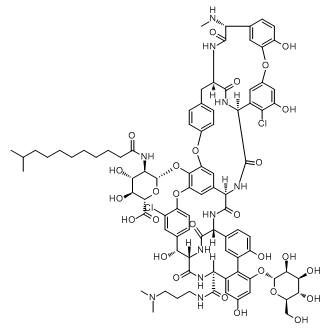
SMILESCC(C)CCCCCCCCC(=O)NC1C(C(C(OC1OC2=C3C=C4C=C2OC5=C(C=C(C=C5)C(C6C(=O)NC(C7=C(C(=CC(=C7)O)OC8C(C(C(C(O8)CO)O)O)O)C9=C(C=CC(=C9)C(C(=O)N6)NC(=O)C4NC(=O)C1C2=C(C(=CC(=C2)OC2=C(C=CC(=C2)C(C(=O)NC(CC2=CC=C(O3)C=C2)C(=O)N1)NC)O)O)Cl)O)C(=O)NCCCN(C)C)O)Cl)C(=O)O)O)O
-
Chemical NameRistomycin A aglycone, 5,31-dichloro-38-de(methoxycarbonyl)-7-demethyl-19-deoxy-56-O-[2-deoxy-2-[(10-methyl-1-oxoundecyl)amino]-β-D-glucopyranuronosyl]-38-[[[3-(dimethylamino)propyl]amino]carbonyl]-42-O-α-D-mannopyranosyl-N15-methyl-
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Chen AY, et al. Int J Clin Pract. 2007 May;61(5):853-63.
2. Boucher HW, et al. N Engl J Med. 2014 Jun 5;370(23):2169-79.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Sultamicillin
Sultamicillin is an orally active double prodrug of Ampicillin/Sulbactan. Sulbactam is a semisynthetic β-Lactamase inhibitor.
-
Metallo β-lactamase ...
Metallo β-lactamase ligand 1 is an inhibitor of class B β-lactamase exhibiting antibacterial activities.
-
Salinomycin sodium
A polyether ionophore antibacterial agent that shows effects on mitochondrial ion translocation and respiration.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


