RVX-208
CAS No. 1044870-39-4
RVX-208( RVX208 | RVX 208 | RVX-208 | Apabetalone )
Catalog No. M10222 CAS No. 1044870-39-4
RVX-208 is a potent BET bromodomain inhibitor with IC50 of 0.510 μM for BD2 in a cell-free assay, about 170-fold selectivity over BD1. Phase 2.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 10MG | 35 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 65 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 107 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 156 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 386 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameRVX-208
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionRVX-208 is a potent BET bromodomain inhibitor with IC50 of 0.510 μM for BD2 in a cell-free assay, about 170-fold selectivity over BD1. Phase 2.
-
DescriptionRVX-208 is a potent BET bromodomain inhibitor with IC50 of 0.510 μM for BD2 in a cell-free assay, about 170-fold selectivity over BD1. Phase 2.(In Vitro):Apabetalone (RVX-208) competes with binding of an acetylated histone peptide to tandem BD1 BD2 protein constructs of the four BET proteins, with IC50s between 0.5 and 1.8 μM. Apabetalone increases the production of ApoA-I in hepatocytes in vitro, which results in increased high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C). Apabetalone selectively binds to bromodomains of the BET (Bromodomain and Extra Terminal) family, competing for a site bound by the endogenous ligand, acetylated lysine, and that this accounts for its pharmacological activity. Apabetalone increases Apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-I) production through an epigenetic mechanism and suggests that BET inhibition may be a promising new approach to the treatment of atherosclerosis. Apabetalone increases ApoA-I expression in liver cells. (In Vivo):In the atherosclerosis prophylactic treatment study design, mice are fed a Western diet concurrent with the treatment with 150 mg/kg/dose b.i.d. for 12 weeks. Mice are sacrificed at 12 weeks after treatment. There is a progressive increase in body weight in both the vehicle treated as well as the Apabetalone (RVX-208) treated groups. However, there is only an increase of 4 g (from 24 g to 28 g) body weight after 12 weeks on Western diet in the Apabetalone treated group whereas this increase is found to be 9 g (25 g-34 g) in the vehicle treated group. The significant decrease in body weight gain in Apabetalone treated mice is not due to decreased feed consumption, suggesting a positive attribute of the molecule. Plasma lipid measurements are done at 6 weeks and 12 weeks of treatment with either the vehicle or Apabetalone. Compared to the vehicle control animals, Apabetalone treated mice show significant increase (~200%) in the levels of HDL-C at 6 weeks of treatment, which is sustained until end of the study (12 weeks).
-
In VitroApabetalone (RVX-208) competes with binding of an acetylated histone peptide to tandem BD1 BD2 protein constructs of the four BET proteins, with IC50s between 0.5 and 1.8 μM. Apabetalone increases the production of ApoA-I in hepatocytes in vitro, which results in increased high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C). Apabetalone selectively binds to bromodomains of the BET (Bromodomain and Extra Terminal) family, competing for a site bound by the endogenous ligand, acetylated lysine, and that this accounts for its pharmacological activity. Apabetalone increases Apolipoprotein A-I (ApoA-I) production through an epigenetic mechanism and suggests that BET inhibition may be a promising new approach to the treatment of atherosclerosis. Apabetalone increases ApoA-I expression in liver cells.
-
In VivoIn the atherosclerosis prophylactic treatment study design, mice are fed a Western diet concurrent with the treatment with 150 mg/kg/dose b.i.d. for 12 weeks. Mice are sacrificed at 12 weeks after treatment. There is a progressive increase in body weight in both the vehicle treated as well as the Apabetalone (RVX-208) treated groups. However, there is only an increase of 4 g (from 24 g to 28 g) body weight after 12 weeks on Western diet in the Apabetalone treated group whereas this increase is found to be 9 g (25 g-34 g) in the vehicle treated group. The significant decrease in body weight gain in Apabetalone treated mice is not due to decreased feed consumption, suggesting a positive attribute of the molecule. Plasma lipid measurements are done at 6 weeks and 12 weeks of treatment with either the vehicle or Apabetalone. Compared to the vehicle control animals, Apabetalone treated mice show significant increase (~200%) in the levels of HDL-C at 6 weeks of treatment, which is sustained until end of the study (12 weeks).
-
SynonymsRVX208 | RVX 208 | RVX-208 | Apabetalone
-
PathwayChromatin/Epigenetic
-
TargetEpigenetic Reader Domain
-
RecptorBD2
-
Research AreaInflammation/Immunology
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1044870-39-4
-
Formula Weight370.4
-
Molecular FormulaC20H22N2O5
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: 74 mg/mL (199.78 mM)
-
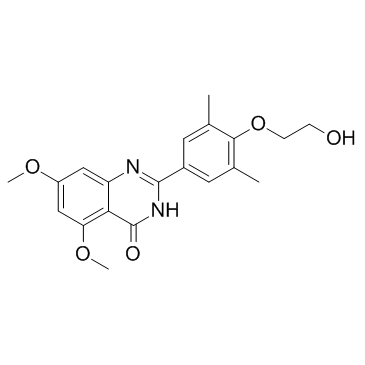
SMILESO=C1NC(C2=CC(C)=C(OCCO)C(C)=C2)=NC3=C1C(OC)=CC(OC)=C3
-
Chemical Name2-(4-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-3,5-dimethylphenyl)-5,7-dimethoxyquinazolin-4(3H)-one
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Picaud S, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013, 110(49), 19754-19759.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Dihydroactinidiolide
Dihydroactinidiolideis avolatileterpene. It has a sweet,tea-likeodorand is used as a fragrance.
-
J147
J-147 is a broad spectrum neuroprotective phenyl hydrazide compound(EC50=60-115 nM) with significant neurotrophic properties related to the induction of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF).
-
GSK046
GSK046 is a potent, selective and orally active BD2 bromodomain inhibitor of the BET proteins(IC50s of 264 nM (BRD2 BD2), 98 nM (BRD3 BD2), 49 nM (BRD4 BD2) and 214 nM (BRDT BD2), respectively).



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


