RSV604
CAS No. 676128-63-5
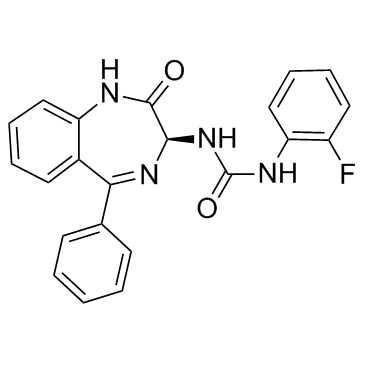
RSV604( (S)-1-(2-Fluorophenyl)-3-(2-oxo-5-phenyl-23-dihydro-1H-benzo[e][14]diazepin-3-yl)urea )
Catalog No. M20757 CAS No. 676128-63-5
RSV-604 is an inhibitor of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) that binds to RSV nucleoprotein (Kd = 1.31 μM).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 31 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 50 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 87 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 178 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 356 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 587 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 824 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameRSV604
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionRSV-604 is an inhibitor of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) that binds to RSV nucleoprotein (Kd = 1.31 μM).
-
DescriptionRSV-604 is an inhibitor of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) that binds to RSV nucleoprotein (Kd = 1.31 μM).(In Vitro):RSV604 (5 days) inhibits the growth of four laboratory strains of RSV (RSS, Long, A2 and B), with EC50s ranging from 0.5 to 0.9 μM in plaque reduction assay.RSV604 (6 days) inhibits RSV-induced HEp-2 cell death, with an EC50 of 0.86 μM.RSV604 (3 days) reduces viral antigen synthesis in RSV-infected HEp-2 cells, with an EC50 of 1.7 μM.RSV604 (1-20 μM; 7 days) dose-dependently inhibits RSV infection in human airway epithelial (HAE) cells, with no gross cytotoxicity, leakage of basolateral fluid to the apical surface, or alteration of cilium beat frequency.
-
In VitroRSV604 (5 days) inhibits the growth of four laboratory strains of RSV (RSS, Long, A2 and B), with EC50s ranging from 0.5 to 0.9 μM in plaque reduction assay.RSV604 (6 days) inhibits RSV-induced HEp-2 cell death, with an EC50 of 0.86 μM.RSV604 (3 days) reduces viral antigen synthesis in RSV-infected HEp-2 cells, with an EC50 of 1.7 μM.RSV604 (1-20 μM; 7 days) dose-dependently inhibits RSV infection in human airway epithelial (HAE) cells, with no gross cytotoxicity, leakage of basolateral fluid to the apical surface, or alteration of cilium beat frequency.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms(S)-1-(2-Fluorophenyl)-3-(2-oxo-5-phenyl-23-dihydro-1H-benzo[e][14]diazepin-3-yl)urea
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorRSV
-
Research AreaMetabolic Disease
-
IndicationRespiratory syncytial virus infections
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number676128-63-5
-
Formula Weight388.39
-
Molecular FormulaC22H17FN4O2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:195 mg/mL (502.07 mM)
-
SMILESFc1ccccc1NC(=O)N[C@H]1N=C(c2ccccc2)c2ccccc2NC1=O
-
Chemical Name(S)-1-(2-fluorophenyl)-3-(2-oxo-5-phenyl-23-dihydro-1H-benzo[e][14]diazepin-3-yl)urea
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.RSV604 a Novel Inhibitor of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Replication[J]. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 2007 51(9):3346-3353.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Anavex 2-73
Anavex 2-73 is a Sigma-1 Receptor agonist (IC50: 860 nM).
-
GB 1b
GB 1b is a natural product isolated from the leaves of Garcinia travancorica.
-
Timosaponin A1
Timosaponin A1 is a coprostane type steroidal saponin isolated from Rhizoma Anemarrhenae.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


