R-7050
CAS No. 303997-35-5
R-7050( R-7050 | R 7050 | R7050 | TNF-α Antagonist III )
Catalog No. M18394 CAS No. 303997-35-5
R-7050 is a tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) antagonist with greater selectivity toward TNFα.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 34 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 55 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 87 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 195 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 267 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 439 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 954 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameR-7050
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionR-7050 is a tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) antagonist with greater selectivity toward TNFα.
-
DescriptionR-7050 is a TNF-α receptor antagonist. It acts by blocking receptor-adaptor molecule complex formation and subsequent receptor internalization, but not TNF-α ligand-receptor binding.(In Vitro):R-7050 (TNF-α Antagonist III) is a potent and fully reversible hit with greater selectivity toward TNFα. In TNFα-induced intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) expression, R-7050 inhibition potency (EC50=0.63 μM) is 2- to 3-fold greater than EC50 for IL-1β-induced ICAM-1 expression (EC50=1.45 2 μM). R-7050 inhibits phosphorylation of both the JNK pathway (MKK4, JNKs, and ATF2) and p38 pathway (MKK3/6, p38, and MAPKAP2). R-7050 is a cell-permeable triazoloquinoxaline compound that selectively inhibits TNF-α induced cellular signaling. Unlike biologic TNF inhibitors (e.g. Infliximab, Etanercept, Adalimumab) that directly bind TNF-α and function as decoy receptors, R-7050 does not affect binding of TNF-α to TNFR. In contrast, R-7050 selectively inhibits the association of TNFR with intracellular adaptor molecules (e.g. TRADD, RIP), limits receptor internalization, and prevents subsequent cellular responses after TNF-α binding. (In Vivo):R-7050 (TNF-α Antagonist III) (6 mg/kg) reduces Evans blue extravasation to 28.7±5.9 μg and 30.3±1.9 μg Evans blue/g brain tissue when administered at 0.5 h or 2 h post-ICH, respectively (p<0.05 and p<0.01 vs ICH, respectively; not significantly different from sham). Brain water content, a measure of brain edema, increases from 75.6±0.3% in sham-operated mice to 81.5±0.5% at 24h post-ICH (p<0.05 vs. sham). 6, 12, or 18 mg/kg R-7050 reduces brain water content to 78.5±0.3%, 78.3±0.3%, or 79.3±0.5%, respectively (all treatments p<0.05 vs. ICH; treatments not significantly different from each other). Notably, mice treated with 18 mg/kg exhibit a reduction in general activity/locomotion. As is observed with Evans blue extravasation, R-7050 (6 mg/kg) significantly reduces brain water content after ICH. Administration of R-7050 at 0.5h or 2h post-ICH attenuates brain water content to levels observed in sham-operated mice (p<0.05 vs ICH, not significantly different from sham).
-
In VitroR-7050 (TNF-α Antagonist III) is a potent and fully reversible hit with greater selectivity toward TNFα. In TNFα-inducedintercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1)expression, R-7050 inhibition potency (EC50=0.63 μM) is 2- to 3-fold greater than EC50 for IL-1β-induced ICAM-1 expression (EC50=1.45 2 μM). R-7050 inhibits phosphorylation of both the JNK pathway (MKK4, JNKs, and ATF2) and p38 pathway (MKK3/6, p38, and MAPKAP2). R-7050 is a cell-permeable triazoloquinoxaline compound that selectively inhibits TNF-α induced cellular signaling. Unlike biologic TNF inhibitors (e.g. Infliximab, Etanercept, Adalimumab) that directly bind TNF-α and function as decoy receptors, R-7050 does not affect binding of TNF-α to TNFR. In contrast, R-7050 selectively inhibits the association of TNFR with intracellular adaptor molecules (e.g. TRADD, RIP), limits receptor internalization, and prevents subsequent cellular responses after TNF-α binding.
-
In VivoR-7050 (TNF-α Antagonist III) (6 mg/kg) reduces Evans blue extravasation to 28.7±5.9 μg and 30.3±1.9 μg Evans blue/g brain tissue when administered at 0.5 h or 2 h post-ICH, respectively (p<0.05 and p<0.01 vs ICH, respectively; not significantly different from sham). Brain water content, a measure of brain edema, increases from 75.6±0.3% in sham-operated mice to 81.5±0.5% at 24h post-ICH (p<0.05 vs. sham). 6, 12, or 18 mg/kg R-7050 reduces brain water content to 78.5±0.3%, 78.3±0.3%, or 79.3±0.5%, respectively (all treatments p<0.05 vs. ICH; treatments not significantly different from each other). Notably, mice treated with 18 mg/kg exhibit a reduction in general activity/locomotion. As is observed with Evans blue extravasation, R-7050 (6 mg/kg) significantly reduces brain water content after ICH. Administration of R-7050 at 0.5h or 2h post-ICH attenuates brain water content to levels observed in sham-operated mice (p<0.05 vs ICH, not significantly different from sham).
-
SynonymsR-7050 | R 7050 | R7050 | TNF-α Antagonist III
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorTNF-α
-
Research AreaCancer
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number303997-35-5
-
Formula Weight380.77
-
Molecular FormulaC16H8ClF3N4S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO : 25 mg/mL 65.66 mM
-
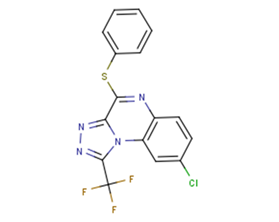
SMILESFC(F)(F)c3nnc2c(nc1ccc(Cl)cc1n23)Sc4ccccc4
-
Chemical Name8-Chloro-4-(phenylthio)-1-(trifluoromethyl)-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]quinoxaline
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Gururaja TL, et al. A class of small molecules that inhibit TNFalpha-induced survival and death pathways viaprevention of interactions between TNFalphaRI, TRADD, and RIP1. Chem Biol. 2007 Oct;14(10):1105-18.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Urolignoside
Urolignoside shows antioxidant and radical scavenging activity.
-
Coelonin
Coelonin shows moderate cytotoxic activity against HepG2 cells.
-
Propargyl-C1-NHS est...
Propargyl-C1-NHS ester is a nonclaevable linker for antibody-drug-conjugation (ADC).



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


