Procainamide
CAS No. 51-06-9
Procainamide( —— )
Catalog No. M35399 CAS No. 51-06-9
Procainamide (Novocainamide) is a specific and potent DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) inhibitor and a Class 1A antiarrhythmic agent, with potential applications in cancer and arrhythmia research .
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 200MG | 30 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameProcainamide
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionProcainamide (Novocainamide) is a specific and potent DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1) inhibitor and a Class 1A antiarrhythmic agent, with potential applications in cancer and arrhythmia research .
-
DescriptionProcainamide is a specific and potent inhibitor of DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1). Procainamide is a Class 1A antiarrhythmic agent. Procainamide has the potential for the research of cancer and arrhythmias.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayCell Cycle/DNA Damage
-
TargetDNA/RNA Synthesis
-
RecptorDNA Methyltransferase
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number51-06-9
-
Formula Weight235.33
-
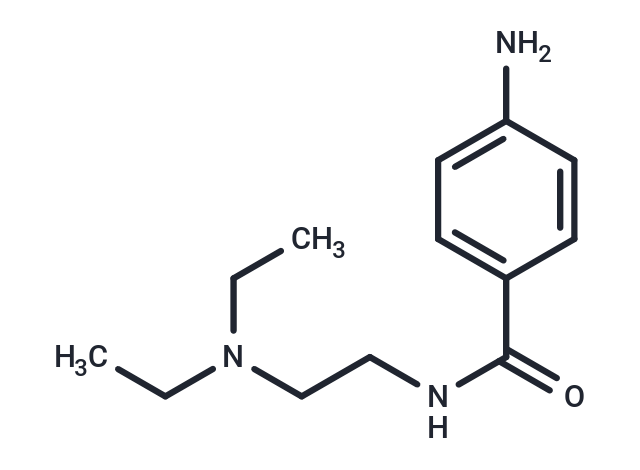
Molecular FormulaC13H21N3O
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 50 mg/mL (212.47 mM; Ultrasonic )
-
SMILESCCN(CC)CCNC(=O)c1ccc(N)cc1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Lee BH, et al. Procainamide is a specific inhibitor of DNA methyltransferase 1. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(49):40749-40756.?
molnova catalog



related products
-
Carmofur
Carmofur is a derivative of fluorouracil, and is an antineoplastic agent that has been used in the treatment of breast and colorectal Y.
-
SMN-C3
SMN-C3 (MV8T2MCK57) is an orally active modulator of SMN2 splicing, and has the potential to treat spinal muscular atrophy (SMA).
-
Nanaomycin A
Nanaomycin A, a quinone antibiotics, reactivates silenced tumor suppressor genes in human cancer cells. Nanaomycin A is a selective inhibitor of DNMT3B (IC50 = 500 nM).



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


