PhIP
CAS No. 105650-23-5
PhIP( —— )
Catalog No. M33464 CAS No. 105650-23-5
PhIP is a heterocyclic aromatic amine (HAA) from cooked meat. It belongs to pyridine heterocyclic amine and is a 2B carcinogen with estrogen activity. PhIP forms adducts with DNA that promote cancer.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 207 | Get Quote |


|
| 5MG | 321 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 487 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 753 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 994 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 1332 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NamePhIP
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionPhIP is a heterocyclic aromatic amine (HAA) from cooked meat. It belongs to pyridine heterocyclic amine and is a 2B carcinogen with estrogen activity. PhIP forms adducts with DNA that promote cancer.
-
DescriptionPhIP is a heterocyclic aromatic amine (HAA) from cooked meat. It belongs to pyridine heterocyclic amine and is a 2B carcinogen with estrogen activity. PhIP forms adducts with DNA that promote cancer.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number105650-23-5
-
Formula Weight224.26
-
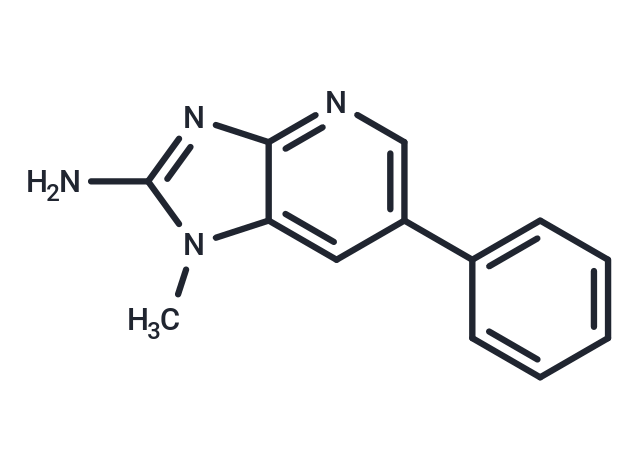
Molecular FormulaC13H12N4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESCn1c(N)nc2ncc(cc12)-c1ccccc1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
D-Xylose
D-Xylose ((2S,3R,4S,5R)-oxane-2,3,4,5-tetrol) is a monosaccharide widely found in yeast and involved in the metabolism of the organism.
-
α-MSH, Free Acid
α-MSH, Free Acid
-
Macrophylloside D
Macrophylloside D is a natural product for research related to life sciences.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


