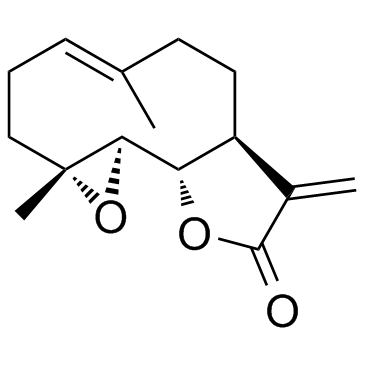
Parthenolide
CAS No. 20554-84-1
Parthenolide( Parthenolide | NSC-157035 | NSC 157035 | NSC157035 )
Catalog No. M13194 CAS No. 20554-84-1
(-)-Parthenolide is a sesquiterpene lactone which occurs naturally in the plant feverfew(Tanacetum parthenium) and also promotes the ubiquitination of MDM2 and activates p53 cellular functions.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 50MG | 45 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 61 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | 107 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameParthenolide
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description(-)-Parthenolide is a sesquiterpene lactone which occurs naturally in the plant feverfew(Tanacetum parthenium) and also promotes the ubiquitination of MDM2 and activates p53 cellular functions.
-
Description(-)-Parthenolide is a sesquiterpene lactone which occurs naturally in the plant feverfew(Tanacetum parthenium) and also promotes the ubiquitination of MDM2 and activates p53 cellular functions.(In Vitro):Parthenolide (PTL) has a dose-dependent growth inhibition effect on NSCLC cells Calu-1, H1792, A549, H1299, H157, and H460. Parthenolide can induce cleavage of apoptotic proteins such as CASP8, CASP9, CASP3 and PARP1 both in concentration- and time-dependent manner in tested lung cancer cells, indicating that apoptosis is trigged after Parthenolide exposure. In addition to induction of apoptosis, Parthenolide also induces G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in a concentration-dependent manner in A549 cells and G2/M cell cycle arrest in H1792 cells.(In Vivo):Only Parthenolide, the HDAC inhibitor with anti-inflammatory features, displayed a potent anti-apoptotic effect in Phb1 KO hepatocytes. Indeed, TSA and Parthenolide-treated hepatocytes showed increased levels of FXR, and reduced levels of CYP7A1, HDAC4, TNFα, TRAIL and Bax suggesting a less toxic effect of bile acids as a results of specific HDAC inhibition, resulting in the attenuation of the Phb1 KO hepatocytes apoptotic response. Importantly, Parthenolide exerts a protective effect from the liver injury after BDL in Phb1 KO mice. Indeed, Parthenolide treatment results in a reduction of the mortality rate of this mice after BDL associated with a lower apoptotic response as revealed by a reduction of necrotic areas, Tunel-staining, as well as decreased ALT (8431±957 vs.4225±210 U/L) and AST (4805±300 vs.2242±438 U/L) activities compared to control Phb1 KO mice.
-
In VitroParthenolide (PTL) has a dose-dependent growth inhibition effect on NSCLC cells Calu-1, H1792, A549, H1299, H157, and H460. Parthenolide can induce cleavage of apoptotic proteins such as CASP8, CASP9, CASP3 and PARP1 both in concentration- and time-dependent manner in tested lung cancer cells, indicating that apoptosis is trigged after Parthenolide exposure. In addition to induction of apoptosis, Parthenolide also induces G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in a concentration-dependent manner in A549 cells and G2/M cell cycle arrest in H1792 cells.
-
In VivoOnly Parthenolide, the HDAC inhibitor with anti-inflammatory features, displayed a potent anti-apoptotic effect in Phb1 KO hepatocytes. Indeed, TSA and Parthenolide-treated hepatocytes showed increased levels of FXR, and reduced levels of CYP7A1, HDAC4, TNFα, TRAIL and Bax suggesting a less toxic effect of bile acids as a results of specific HDAC inhibition, resulting in the attenuation of the Phb1 KO hepatocytes apoptotic response. Importantly, Parthenolide exerts a protective effect from the liver injury after BDL in Phb1 KO mice. Indeed, Parthenolide treatment results in a reduction of the mortality rate of this mice after BDL associated with a lower apoptotic response as revealed by a reduction of necrotic areas, Tunel-staining, as well as decreased ALT (8431±957 vs.4225±210 U/L) and AST (4805±300 vs.2242±438 U/L) activities compared to control Phb1 KO mice.
-
SynonymsParthenolide | NSC-157035 | NSC 157035 | NSC157035
-
PathwayApoptosis
-
TargetNF-κB
-
RecptorNF-κB
-
Research AreaCancer
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number20554-84-1
-
Formula Weight248.32
-
Molecular FormulaC15H20O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityEthanol: 50 mg/mL (201.35 mM); DMSO: 50 mg/mL (201.35 mM)
-
SMILESO=C(O[C@@]1([H])[C@@]2([H])CC/C(C)=C/CC[C@]3(C)[C@]1([H])O3)C2=C
-
Chemical Name(3aS,9aR,10aR,10bS,E)-6,9a-dimethyl-3-methylene-3a,4,5,8,9,9a,10a,10b-octahydrooxireno[2',3':9,10]cyclodeca[1,2-b]furan-2(3H)-one
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Lin M, et al. Parthenolide suppresses non-small cell lung cancer GLC-82 cells growth via B-Raf/MAPK/Erk pathway. Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 4;8(14):23436-23447.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Amgen16
Amgen 16 (Amgen16) is a highly potent inhibitor of NF-κB inducing Kinase (NIK) with Ki of 2 nM.
-
Saikosaponin A
Extracted from Bupleurum,scorzonerifolium;Suitability:Water,dilute alcohol,especially the hot water,hot alcohol,butanol and pentanol;Store the product in sealed,cool and dry condition
-
BAY 11-7082
BAY 11-7082 a NF-κB inhibitor that selectively and irreversibly inhibits the TNF-α-inducible phosphorylation of IκBα (IC50=10 uM).



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


