PKR-IN-C16
CAS No. 608512-97-6
PKR-IN-C16( —— )
Catalog No. M22715 CAS No. 608512-97-6
PKR-IN-C16 is a specific protein kinase (PKR) inhibitor. PKR-IN-C16 is able to inhibit the autophosphorylation of PKR and unlock the translation blockade induced by PKR in primary neuronal cultures.PKR-IN-C16 binds the ATP-binding site of PKR and blocks autophosphorylation with an IC50 value of 186-210 nM.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 46 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 72 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 125 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 260 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 410 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 605 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NamePKR-IN-C16
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionPKR-IN-C16 is a specific protein kinase (PKR) inhibitor. PKR-IN-C16 is able to inhibit the autophosphorylation of PKR and unlock the translation blockade induced by PKR in primary neuronal cultures.PKR-IN-C16 binds the ATP-binding site of PKR and blocks autophosphorylation with an IC50 value of 186-210 nM.
-
DescriptionPKR-IN-C16 is a specific protein kinase (PKR) inhibitor. PKR-IN-C16 is able to inhibit the autophosphorylation of PKR and unlock the translation blockade induced by PKR in primary neuronal cultures.PKR-IN-C16 binds the ATP-binding site of PKR and blocks autophosphorylation with an IC50 value of 186-210 nM. PKR-IN-C16 protects human neuroblastoma cells against cell damage triggered by tunicamycin-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress.
-
In VitroPKR-IN-C16 (Compound C16) is able to unlock the translation blockade induced by PKR in primary neuronal cultures.PKR-IN-C16 (0.1 or 0.3 μM; 24 h) shows protective effect against the neuronal cell death induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress in SH-SY5Y cells.?PKR-IN-C16 (1-1000 nM; 4 h) prevents not only PKR-phosphorylation but also the activation of caspase-3 induced by Amyloid β in SH-SY5Y cells. Western Blot Analysis Cell Line:Human SH-SY5Y cells Concentration:1, 10, 20, 200, 1000 nM Incubation Time:4 h Result:Markedly reduces the level of phosphorylated PKR in the cells exposed to 20 μM Amyloid β.
-
In VivoPKR-IN-C16 (Compound C16) (60 or 600 μg/kg; i.p.; 3 times) prevents not only the PKR-induced neuronal loss but also the inflammatory response in the Quinolinic acid (QA) (HY-100807) induced acute excitotoxic rat model Animal Model:Normotensive male Wistar rats, excitotoxic neuroinflammatory model, inflammation was induced by unilateral striatal injection of quinolinic acid (QA)Dosage:60 or 600 μg/kg Administration: Intraperitoneal injection; 24 h, 2 h before QA injection and 24 h post-QA injectionResult:Reduced expression of the active catalytic domain of the PKR, prevented increase of IL-1β levels on the contralateral side (97% inhibition) at 600 μg/kg. Decreased by 47% the neuronal loss and by 37% the number of positive cleaved caspase-3 neurons induced by QA injection at 600 μg/kg.
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorPKR
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number608512-97-6
-
Formula Weight268.29
-
Molecular FormulaC13H8N4OS
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:15.67 mg/mL(58.41 mM)
-
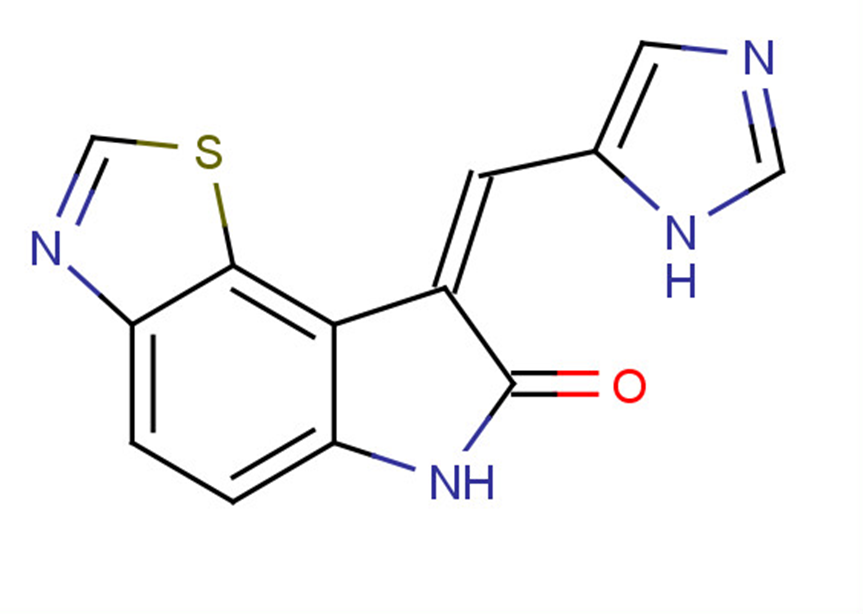
SMILESO=C1Nc2ccc3ncsc3c2\C1=C\c1cnc[nH]1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Tronel C, et al. The specific PKR inhibitor C16 prevents apoptosis and IL-1β production in an acute excitotoxic rat model with a neuroinflammatory component. Neurochem Int. 2014 Jan;64:73-83.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Shikonin
Alkannin is a natural dye that is obtained from the extracts of plants from the borage family Alkanna tinctoria that are found in the south of France.
-
Glembatumumab vedoti...
Glembatumumab vedotin (CDX-011) is an antibody-drug conjugate with potent anticancer effects, utilized in the study of triple negative breast cancer (TNBC).
-
Carasinol D
Carasinol D is a natural product from Carex humilis Leyss.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


