PIK-293
CAS No. 900185-01-5
PIK-293( PIK-293 | PIK 293 | PIK293 )
Catalog No. M17650 CAS No. 900185-01-5
PIK-293 is a?PI3K?inhibitor, for?PI3Kδ( IC50=0.24 μM), and less potent for PI3Kα/β/ γ.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 67 | In Stock |


|
| 5MG | 110 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 177 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 312 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 464 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 662 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NamePIK-293
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionPIK-293 is a?PI3K?inhibitor, for?PI3Kδ( IC50=0.24 μM), and less potent for PI3Kα/β/ γ.
-
DescriptionPIK-293 is a?PI3K?inhibitor, for?PI3Kδ( IC50=0.24 μM), and less potent for PI3Kα/β/ γ.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsPIK-293 | PIK 293 | PIK293
-
PathwayMAPK/ERK Signaling
-
TargetJNK
-
Recptorp110α| p110β| p110γ| p110δ
-
Research AreaCancer
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number900185-01-5
-
Formula Weight397.43
-
Molecular FormulaC22H19N7O
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 50 mg/mL (125.81 mM)
-
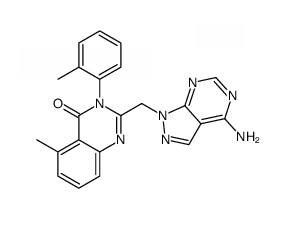
SMILESCc1c2c(ccc1)nc(n(c2=O)c1ccccc1C)Cn1c2c(cn1)c(ncn2)N
-
Chemical Name2-((4-amino-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-1-yl)methyl)-5-methyl-3-o-tolylquinazolin-4(3H)-one
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Knight ZA et al. Cell, 2006, 125(4), 733-747.
molnova catalog



related products
-
d-Epigalbacin
d-Epigalbacin is a naturally occurring lignin. d-Epigalbacin is a potent, selective JNKs inhibitor, with IC50s of 1.7 μM, 2.9 μM and 1.74 μM for JNK1, JNK2 and JNK3, respectively.
-
AS601245.2TFA
AS601245.2TFA is a cell-permeable Inhibitor of JNK (IC50s of 150, 220, and 70 nM for hJNK1, hJNK2, and hJNK3, respectively).
-
JNK-IN-11
JNK-IN-11 (compound 1) is a potent inhibitor of JNK, with IC50 values of 2.2 μM, 21.4 μM, and 1.8 μM for JNK1, JNK2, and JNK3, respectively, showing potential for Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease research.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


