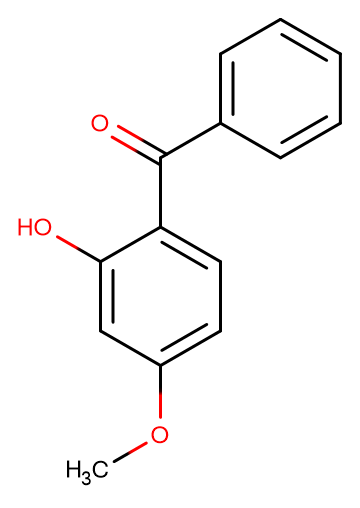
Oxybenzone
CAS No. 131-57-7
Oxybenzone( Oxybenzone, Benzophenone-3, 2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzone, Eusolex-4360 )
Catalog No. M11279 CAS No. 131-57-7
Oxybenzone is an organic compound used in sunscreens. It is a derivative of benzophenone.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 500MG | 39 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameOxybenzone
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionOxybenzone is an organic compound used in sunscreens. It is a derivative of benzophenone.
-
DescriptionOxybenzone is an organic compound used in sunscreens. It is a derivative of benzophenone. It forms colorless crystals that are readily soluble in most organic solvents. It is used as an ingredient in sunscreen and other cosmetics because it absorbs UV-A ultraviolet rays. (In Vitro):Oxybenzone (Benzophenone 3) (25 μM; 24 hours) decreases the relative RXRβ and RXRγ protein levels by 61 and 56%, respectively and increases the relative RXRα protein level by 49%.Oxybenzone (25-100 μM; 24 hours) induces an increase in caspase-3 levels in primary cultures of mouse neocortical cells at 7 DIV. Oxybenzone-induced apoptosis involves the activation of RXRα signaling and the impairment of RXRβ/RXRγ signaling. Oxybenzone (25 μM; 24 hours) inhibits global DNA methylation as well as reduced HDAC and HAT activities in mouse embryonic neuronal cells.
-
In VitroOxybenzone (Benzophenone 3) (25 μM; 24 hours) decreases the relative RXRβ and RXRγ protein levels by 61 and 56%, respectively and increases the relative RXRα protein level by 49%.Oxybenzone (25-100 μM; 24 hours) induces an increase in caspase-3 levels in primary cultures of mouse neocortical cells at 7 DIV. Oxybenzone-induced apoptosis involves the activation of RXRα signaling and the impairment of RXRβ/RXRγ signaling. Oxybenzone (25 μM; 24 hours) inhibits global DNA methylation as well as reduced HDAC and HAT activities in mouse embryonic neuronal cells. Western Blot Analysis Cell Line:Mouse neocortical cells at 7 DIV Concentration:25 μM Incubation Time:24 hours Result:Exposure to Oxybenzone (25 μM) for 24 h decreased the relative RXRβ and RXRγ protein levels by 61 and 56%, respectively. Treatment with Oxybenzone (25 μM) increased the relative RXRα protein level by 49%.
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsOxybenzone, Benzophenone-3, 2-hydroxy-4-methoxybenzone, Eusolex-4360
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number131-57-7
-
Formula Weight228.24
-
Molecular FormulaC14H12O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityWater: 69 mg/L .
-
SMILESO=C(C1=CC=C(OC)C=C1O)C2=CC=CC=C2
-
Chemical Name(2-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)-phenylmethanone
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Gonzalez H, et al. Br J Dermatol. 2006 Feb;154(2):337-40.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Ophiogenin 3-O-α-L-r...
Ophiogenin 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-glucopyranoside is a natural product, and has good pharmacological effects on the cardiovascular system.
-
Latrepirdine
Latrepirdine is an orally active, and neuroactive antagonist of multiple drug targets, including histamine receptors, GluR, and 5-HT receptors, used as an antihistamine drug.
-
6-Aminocaproic acid
6-Aminocaproic acid is an antifibrinolytic agent that acts by inhibiting plasminogen activators which have fibrinolytic properties.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


