NS1652
CAS No. 1566-81-0
NS1652( —— )
Catalog No. M22621 CAS No. 1566-81-0
NS1652 is an anion conductance inhibitor. NS1652 blocks chloride channel has an IC50 of 1.6 μM in human and mouse red blood cells.NS1652 (20 μM) fully and reversibly inhibits the red cell Cl-conductance. NS1652 effectively inhibits the chloride conductance (IC50, 1.6 μM) in human and mouse red blood cells, but only weakly inhibits VRAC (IC50, 125 μM) in HEK293 cells. NS1652 markedly blocks the NO production (IC50: 3.1 μM in BV2 cells).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 160 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 259 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 485 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 700 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 954 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 1908 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameNS1652
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionNS1652 is an anion conductance inhibitor. NS1652 blocks chloride channel has an IC50 of 1.6 μM in human and mouse red blood cells.NS1652 (20 μM) fully and reversibly inhibits the red cell Cl-conductance. NS1652 effectively inhibits the chloride conductance (IC50, 1.6 μM) in human and mouse red blood cells, but only weakly inhibits VRAC (IC50, 125 μM) in HEK293 cells. NS1652 markedly blocks the NO production (IC50: 3.1 μM in BV2 cells).
-
DescriptionNS1652 is an anion conductance inhibitor. NS1652 blocks chloride channel has an IC50 of 1.6 μM in human and mouse red blood cells.NS1652 (20 μM) fully and reversibly inhibits the red cell Cl-conductance. NS1652 effectively inhibits the chloride conductance (IC50, 1.6 μM) in human and mouse red blood cells, but only weakly inhibits VRAC (IC50, 125 μM) in HEK293 cells. NS1652 markedly blocks the NO production (IC50: 3.1 μM in BV2 cells). NS1652 also down-regulates iNOS expression at 3 μM and fully abolishes at 10 μM in BV2 cells. NS1652 (0, 1.0, 3.3, 10, and 20 μM) induces increasing hyperpolarization due to inhibition of the chloride conductance in normal erythrocytes. NS1652 lowers the net KCl loss from deoxygenated sickle cells from about 12 mM cells/h to about 4 mM cells/h. In mice, NS1652 (50 mg/kg, i.v.) blocks murine erythrocyte Cl- conductance by >90%.
-
In VitroNS1652 potently inhibits the chloride conductance (IC50, 1.6 μM) in human and mouse red blood cells, but only weakly inhibits VRAC (IC50, 125 μM) in HEK293 cells. NS1652 markedly blocks the NO production with an IC50 of 3.1 μM in BV2 cells. NS1652 also down-regulates iNOS expression at 3 μM, and completely abolishes at 10 μM in BV2 cells. NS1652 (0, 1.0, 3.3, 10, and 20 μM) causes increasing hyperpolarization due to inhibition of the chloride conductance in normal erythrocytes. NS1652 lowers the net KCl loss from deoxygenated sickle cells from about 12 mM cells/h to about 4 mM cells/h. NS1652 (20 μM) completely and reversiblely inhibits the red cell Cl-conductance.
-
In VivoNS1652 (50 mg/kg, i.v.) blocks murine erythrocyte Cl- conductance by >90% in mice.
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayMembrane Transporter/Ion Channel
-
TargetChloride Channel
-
Recptorchloride channel
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number1566-81-0
-
Formula Weight324.25
-
Molecular FormulaC15H11F3N2O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:4.9 mg/mL (15.11 mM; Need ultrasonic)
-
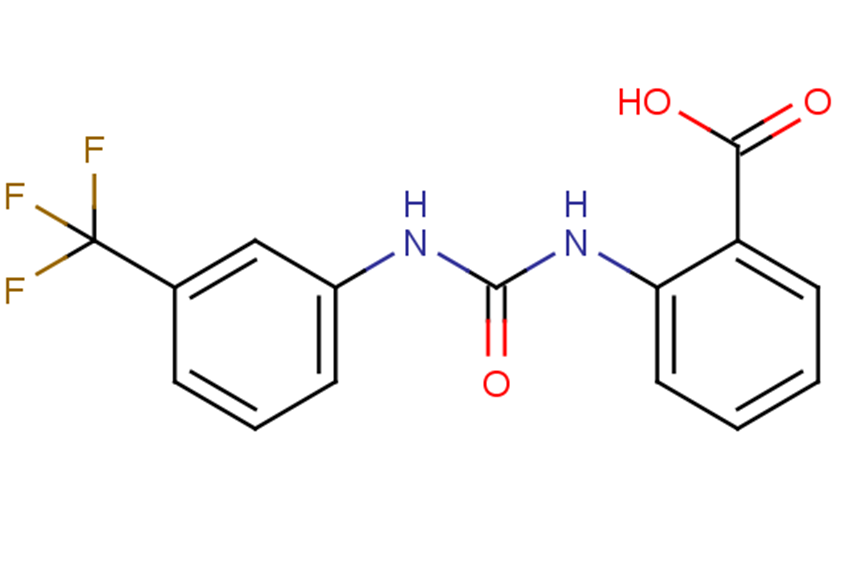
SMILESOC(=O)c1ccccc1NC(=O)Nc1cccc(c1)C(F)(F)F
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Kjaer K, et al. Chloride channel blockers inhibit iNOS expression and NO production in IFNgamma-stimulated microglial BV2 cells. Brain Res. 2009 Jul 24;1281:15-24.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Org 25543
Org 25543 is the development of an N-Acyl amino acid that selectively inhibits the glycine transporter 2 to produce analgesia in a rat model of chronic pain.
-
GaTx2
Very high affinity ClC-2 blocker (apparent KD ~ 50 pM). Slows ClC-2 activation and inhibits slow-gating but does not inhibit open ClC-2 channels. Selective for ClC-2 over other ClC family members (ClC-0, ClC-1, ClC-3 and ClC-4), CFTR, GABAC, CaCC and KV1.2.
-
CLP290
CLP290 (CLP-290) is an orally acirtve small molecule K+-Cl- cotransporter isotype 2 (KCC2) activator, the carbamate prodrug of CLP257.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


