ZINC00881524
CAS No. 557782-81-7
ZINC00881524( ZINC00881524 | ZINC-00881524 | ZINC 00881524 )
Catalog No. M17542 CAS No. 557782-81-7
ZINC00881524 is an effective and specific ROCK inhibitor.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 27 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 42 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 87 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 132 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 203 | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 507 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameZINC00881524
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionZINC00881524 is an effective and specific ROCK inhibitor.
-
DescriptionZINC00881524 is a potent and selective ROCK inhibitor. Clinically, inhibition of ROCK pathway is believed to contribute to some of the cardiovascular benefits of statin therapy that are independent of lipid lowering (ie, pleiotropic effects).
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsZINC00881524 | ZINC-00881524 | ZINC 00881524
-
PathwayMembrane Transporter/Ion Channel
-
TargetChloride Channel
-
RecptorROCK
-
Research AreaOthers-Field
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number557782-81-7
-
Formula Weight380.46
-
Molecular FormulaC21H20N2O3S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO : ≥ 300 mg/mL; 788.52 mM
-
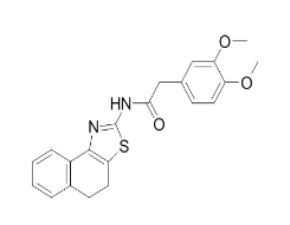
SMILESO=C(Nc1nc2c(CCc3c2cccc3)s1)Cc1ccc(OC)c(OC)c1
-
Chemical NameN-(4,5-dihydronaphtho[1,2-d]thiazol-2-yl)-2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)acetamide
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
CLP257
CLP257 (CLP-257) is a potent, selective K+-Cl- cotransporter KCC2 activator with EC50 of 616 nM.
-
CLP290
CLP290 (CLP-290) is an orally acirtve small molecule K+-Cl- cotransporter isotype 2 (KCC2) activator, the carbamate prodrug of CLP257.
-
Fenamic acid
Fenamic acid is a chloride channel blocker that causes renal papillary necrosis in rats. Fenamic acid serves as a parent structure for several nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including flufenamic acid, tolfenamic acid, mefenamic acid, and meclofenamic acid.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


