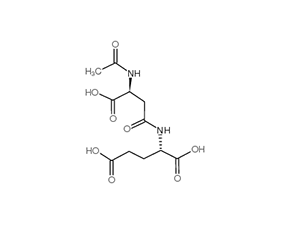
N-Acetyl-β-Asp-Glu
CAS No. 4910-46-7
N-Acetyl-β-Asp-Glu( Spaglumic Acid | Naaxia )
Catalog No. M18644 CAS No. 4910-46-7
Spaglumic acid is the β-aspartyl isoform of N-Acetyl-l-aspartylglutamate (isospaglumic Acid is N-(N-Acetyl-l-α-aspartyl)-l-glutamic acid).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 50MG | 45 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 54 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameN-Acetyl-β-Asp-Glu
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionSpaglumic acid is the β-aspartyl isoform of N-Acetyl-l-aspartylglutamate (isospaglumic Acid is N-(N-Acetyl-l-α-aspartyl)-l-glutamic acid).
-
DescriptionSpaglumic acid is the β-aspartyl isoform of N-Acetyl-l-aspartylglutamate (isospaglumic Acid is N-(N-Acetyl-l-α-aspartyl)-l-glutamic acid). In eye drops, spaglumic acid is either a magnesium or sodium salt of N-Acetyl-l-aspartylglutamate. Spaglumic acid is a mast cell stabilizer. Thus it is used in allergic conditions such as allergic conjunctivitis.
-
In Vitroβ-Spaglumic acid (63-1000 μM; 2 h) protects against NMDA-induced injury of spinal cord cells in a dose-dependent manner.β-Spaglumic acid (0-1000 μM; 2 h) protects spinal cord cells against hypoxia.β-Spaglumic acid (500 μM) significantly reduces intraneuronal free Ca2+ responses upon neuronal exposure to 25 μM NMDA.β-Spaglumic acid (100 μM; 7 min) antagonizes mGluR3 in cerebellar granule cells. Cell Viability Assay Cell Line:Spinal cord cells (NMDA-induced) (from spinal cords removed from prenatal day 15 Sprague-Dawley rat fetuses)Concentration:63-1000 μM Incubation Time:2 h Result:Led to a significant attenuation of NMDA toxicity at a concentration of 63 μM and completely blocked NMDA toxicity with 500 and 1000 μM concentrations.Apparently minimized the basal loss of cell viability associated with experimental handling of the cells (e.g. serum removal, media changes).Cell Viability Assay Cell Line:Spinal cord cells (hypoxic-induced)Concentration:0-1000 μM Incubation Time:2 h Result:Provided 75% protection during hypoxia when at 8 μM and completely eliminated hypoxia-induced loss of viability (107.4-114.4% protection, respectively) when at 63-1000 μM.Cell Viability Assay Cell Line:Cerebellar granule cells (expressing group I-III mGluRs)Concentration:100 μM Incubation Time:7 minResult:Blocked NAAG inhibition of forskolin-stimulated cAMP formation via mGluR3.
-
In Vivo——
-
SynonymsSpaglumic Acid | Naaxia
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorAmino Acids and Derivatives
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number4910-46-7
-
Formula Weight304.25
-
Molecular FormulaC11H16N2O8
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESCC(=O)N[C@@H](CC(=O)N[C@@H](CCC(=O)O)C(=O)O)C(=O)O
-
Chemical Name(S)-1-(((S)-3-acetamido-3-(carboxyoxy)propyl)amino)propane-1,3-diyl bis(hydrogen carbonate)
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
3,4-(Methylenedioxy)...
3,4-(Methylenedioxy)cinnamic acid is a plant-derived compound first extracted from roots of Asparagus officinalis and further characterized as an allelochemical.
-
Biotin-LC-LC-NHS
Biotin-LC-LC-NHS, an SMCC cross-linking reagent, acts as a labeling agent for antibodies and small molecules (like Paclitaxel).
-
WYE-687
WYE-687 is an ATP-competitive and selective inhibitor of mTOR with IC50 of 7 nM; blocks mTORC1/pS6K(T389) and mTORC2/P-AKT(S473) but no effect observed on P-AKT(T308).



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


