Motesanib
CAS No. 453562-69-1
Motesanib( AMG 706 | AMG-706 )
Catalog No. M14539 CAS No. 453562-69-1
A potent, orally bioavailable, multikinase inhibitor inhibitor of VEGFR1/2/3, PDGFR and c-Kit with IC50 of 2-6 nM, 84 nM and 8 nM, respectively.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 33 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 49 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 157 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameMotesanib
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionA potent, orally bioavailable, multikinase inhibitor inhibitor of VEGFR1/2/3, PDGFR and c-Kit with IC50 of 2-6 nM, 84 nM and 8 nM, respectively.
-
DescriptionA potent, orally bioavailable, multikinase inhibitor inhibitor of VEGFR1/2/3, PDGFR and c-Kit with IC50 of 2-6 nM, 84 nM and 8 nM, respectively; also displays activity against Ret (IC50=59 nM), no activities against EGFR, Src, and p38; inhibits human endothelial cell proliferation induced by VEGF, but not by bFGF in vitro; potently inhibits VEGF-induced angiogenesis in the rat models.Lung Cancer Phase 3 Discontinued(In Vitro):Motesanib has broad activity against the human VEGFR family, and displays > 1000 selectivity against EGFR, Src, and p38 kinase. Motesanib significantly inhibits VEGF-induced cellular proliferation of HUVECs with an IC50 of 10 nM, while displaying little effect at bFGF-induced proliferation with an IC50 of >3,000 nM. Motesanib also potently inhibits PDGF-induced proliferation and SCF-induced c-kit phosphorylation with IC50 of 207 nM and 37 nM, respectively, but not effective against the EGF-induced EGFR phosphorylation and cell viability of A431 cells. Althouth displaying little antiproliferative activity on cell growth of HUVECs alone, Motesanib treatment significantly sensitizes the cells to fractionated radiation. (In Vivo):Motesanib (100 mg/kg) significantly inhibits VEGF-induced vascular permeability in a time-dependent manner. Oral administration of Motesanib twice daily or once daily potently inhibits, in a dose-dependent manner, VEGF-induced angiogenesis using the rat corneal model with ED50 of 2.1 mg/kg and 4.9 mg/kg, respectively. Motesanib induces a dose-dependent tumor regression of established A431 xenografts by selectively targeting neovascularization in tumor cells. Motesanib in combination with radiation displays significant anti-tumor activity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) xenograft models. Motesanib treatment also induces significant dose-dependent reductions in tumor growth and blood vessel density of MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, or Cal-51 xenografts, which can be markedly enhanced when combined with docetaxel or tamoxifen.
-
In VitroMotesanib has broad activity against the human VEGFR family, and displays > 1000 selectivity against EGFR, Src, and p38 kinase. Motesanib significantly inhibits VEGF-induced cellular proliferation of HUVECs with an IC50 of 10 nM, while displaying little effect at bFGF-induced proliferation with an IC50 of >3,000 nM. Motesanib also potently inhibits PDGF-induced proliferation and SCF-induced c-kit phosphorylation with IC50 of 207 nM and 37 nM, respectively, but not effective against the EGF-induced EGFR phosphorylation and cell viability of A431 cells.?Althouth displaying little antiproliferative activity on cell growth of HUVECs alone, Motesanib treatment significantly sensitizes the cells to fractionated radiation.
-
In VivoMotesanib (100 mg/kg) significantly inhibits VEGF-induced vascular permeability in a time-dependent manner. Oral administration of Motesanib twice daily or once daily potently inhibits, in a dose-dependent manner, VEGF-induced angiogenesis using the rat corneal model with ED50 of 2.1 mg/kg and 4.9 mg/kg, respectively. Motesanib induces a dose-dependent tumor regression of established A431 xenografts by selectively targeting neovascularization in tumor cells. Motesanib in combination with radiation displays significant anti-tumor activity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) xenograft models.?Motesanib treatment also induces significant dose-dependent reductions in tumor growth and blood vessel density of MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, or Cal-51 xenografts, which can be markedly enhanced when combined with docetaxel or tamoxifen.
-
SynonymsAMG 706 | AMG-706
-
PathwayAngiogenesis
-
TargetVEGFR
-
RecptorVEGFR1|VEGFR2|VEGFR3
-
Research AreaCancer
-
IndicationLung Cancer
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number453562-69-1
-
Formula Weight373.4509
-
Molecular FormulaC22H23N5O
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: ≥ 30 mg/mL
-
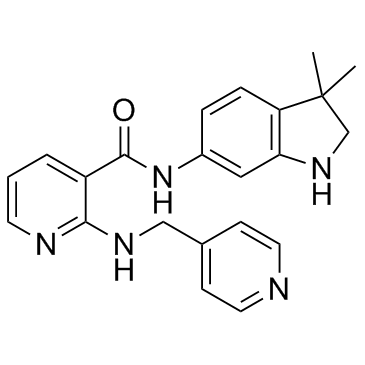
SMILESCC1(CNC2=C1C=CC(=C2)NC(=O)C3=C(N=CC=C3)NCC4=CC=NC=C4)C
-
Chemical Name3-Pyridinecarboxamide, N-(2,3-dihydro-3,3-dimethyl-1H-indol-6-yl)-2-[(4-pyridinylmethyl)amino]-
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Polverino A, et al. Cancer Res. 2006 Sep 1;66(17):8715-21.
2. Sherman SI, et al. N Engl J Med. 2008 Jul 3;359(1):31-42.
3. Coxon A, et al. lin Cancer Res. 2009 Jan 1;15(1):110-8.
4. Caenepeel S, et al. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Jul 15;29:96.
molnova catalog



related products
-
SU5204
SU5204, an analogue of SU5025, pharmacologically inhibits VEGFR2(IC50s of 4 and 51.5 μM for FLK-1 (VEGFR-2) and HER2).
-
TIE-2/VEGFR-2 kinase...
TIE-2/VEGFR-2 kinase-IN-5 (TIE-2 and VEGFR-2 tyrosine kinase receptor inhibitor) is a potent agent with anti-angiogenic activity, commonly used in biomedical research focused on angiogenesis.
-
Linifanib
A potent multi-RTKs inhibitor of members of VEGFR and PDGFR families.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


