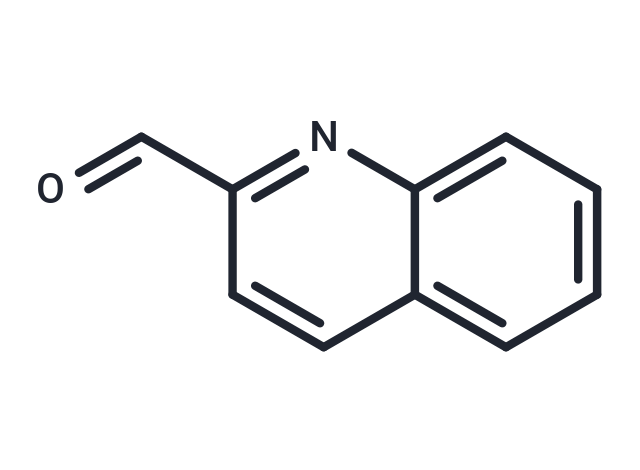
2-Quinolinecarboxaldehyde
CAS No. 5470-96-2
2-Quinolinecarboxaldehyde( —— )
Catalog No. M36399 CAS No. 5470-96-2
2-Quinolinecarboxaldehyde (Quinoline-2-carbaldehyde) is a small rigid molecule that is a compound in the Henry reaction and subsequent elimination.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 27 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name2-Quinolinecarboxaldehyde
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description2-Quinolinecarboxaldehyde (Quinoline-2-carbaldehyde) is a small rigid molecule that is a compound in the Henry reaction and subsequent elimination.
-
DescriptionQuinoline-2-carboxaldehyde is a biochemical reagent that can be used as a biological material or organic compound for life science related research.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayMetabolic Enzyme/Protease
-
TargetAChE
-
RecptorAChE
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number5470-96-2
-
Formula Weight157.17
-
Molecular FormulaC10H7NO
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (636.25 mM; Ultrasonic )
-
SMILESO=CC1=NC2=CC=CC=C2C=C1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Malathion
Malathion is an organophosphate parasympathomimetic which binds irreversibly to cholinesterase, is an insecticide of relatively low human toxicity.
-
Simpinicline
Simpinicline (OC-02) (OC-02) is a highly selective nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) agonist that activates the trigeminal parasympathetic pathway and can be used to treat dry eye.
-
Ipidacrine hydrochlo...
Ipidacrine hydrochloride is a reversible acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


