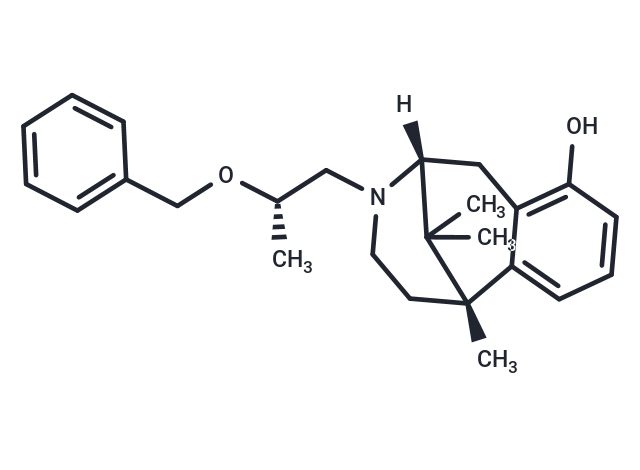
Crobenetine
CAS No. 221019-25-6
Crobenetine( —— )
Catalog No. M36311 CAS No. 221019-25-6
Crobenetine (BIII 890 CL) Free Base is a selective NaV channel blocker that eliminates VTD-induced [Ca2+] elevation.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 719 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 1007 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 1501 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 1981 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameCrobenetine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionCrobenetine (BIII 890 CL) Free Base is a selective NaV channel blocker that eliminates VTD-induced [Ca2+] elevation.
-
DescriptionCrobenetine (BIII 890 CL) Free Base is a selective NaV channel blocker that eliminates VTD-induced [Ca2+] elevation.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayMembrane Transporter/Ion Channel
-
TargetSodium Channel
-
RecptorSodium Channel | Calcium Channel
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number221019-25-6
-
Formula Weight379.54
-
Molecular FormulaC25H33NO2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESC[C@]12C=3C(C[C@](C1(C)C)(N(C[C@@H](OCC4=CC=CC=C4)C)CC2)[H])=C(O)C=CC3
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Amiloride hydrochlor...
A pyrazine compound inhibiting SODIUM reabsorption through SODIUM CHANNELS in renal EPITHELIAL CELLS.
-
Silperisone HCl
Silperisone HCl (RGH-5002) blocks sodium and calcium channels in cells, decreases excitability and contractility of muscle cells, reduces peripheral tone, and acts as a muscle relaxant and peripheral vasodilator.
-
PF-04531083
PF-04531083 (PF 4531083) is a potent and selective, orally available sodium channel Nav1.8 blocker for treatment of pain.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


