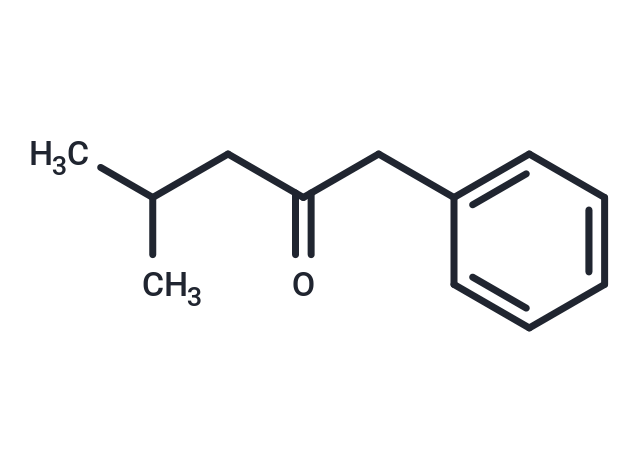
4-Methyl-1-phenyl-2-pentanone
CAS No. 5349-62-2
4-Methyl-1-phenyl-2-pentanone( —— )
Catalog No. M35920 CAS No. 5349-62-2
4-Methyl-1-phenyl-2-pentanone (Benzyl isobutyl ketone) is a volatile flavor compound utilized as a food additive.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 27 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name4-Methyl-1-phenyl-2-pentanone
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description4-Methyl-1-phenyl-2-pentanone (Benzyl isobutyl ketone) is a volatile flavor compound utilized as a food additive.
-
Description4-Methyl-1-phenyl-2-pentanone is an endogenous metabolite.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorEndogenous Metabolite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number5349-62-2
-
Formula Weight176.25
-
Molecular FormulaC12H16O
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 50 mg/mL (283.69 mM; Ultrasonic )
-
SMILESCC(C)CC(=O)Cc1ccccc1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
3-Hydroxypicolinic a...
3-Hydroxypicolinic acid is a picolinic acid derivative and belongs to the pyridine family.
-
3-?Oxocholic acid
3-Oxocholic acid(3-Ketocholic acid) is the metabolite of bile acid and the main product of bile degradation by Clostridium perfringens in the intestine.3-Oxocholic acid is a steroid acid mainly found in the bile of mammals.
-
(R)-3-Hydroxybutanoi...
(R)-3-Hydroxybutanoic acid sodium ((R)-3-Hydroxybutyric acid) is a chiral precursor that can be used to synthesize biodegradable PHB and its copolyesters. (R)-3-Hydroxybutanoic acid sodium can be used as a nutrient in plants.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


