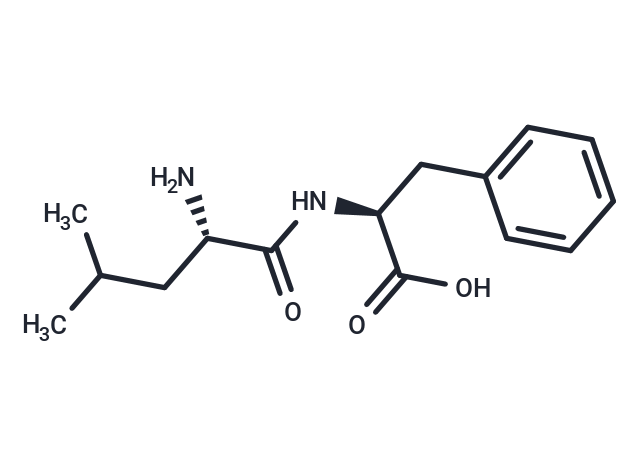
Leucyl-phenylalanine
CAS No. 3063-05-6
Leucyl-phenylalanine( —— )
Catalog No. M33609 CAS No. 3063-05-6
Leucyl-phenylalanine (H-LEU-PHE-OH) is a dipeptide compound that can be used for protein synthesis.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 10MG | 28 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameLeucyl-phenylalanine
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionLeucyl-phenylalanine (H-LEU-PHE-OH) is a dipeptide compound that can be used for protein synthesis.
-
DescriptionLeucyl-phenylalanine belongs to the class of organic compounds known as dipeptides.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorEndogenous Metabolite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number3063-05-6
-
Formula Weight278.35
-
Molecular FormulaC15H22N2O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?H2O : 4 mg/mL (14.37 mM; Ultrasonic)Ethanol : 1.11 mg/mL (3.99 mM; Ultrasonic)DMSO : < 1 mg/mL (insoluble or slightly soluble)
-
SMILESC([C@H](NC([C@H](CC(C)C)N)=O)C(O)=O)C1=CC=CC=C1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Stigmastanol
Stigmastanol is a phytosterol isolated from Hypericum riparium, which is a Cameroonian medicinal plant.
-
Petroselinic acid
Petroselinic acid is a monounsaturated omega-12 fatty acid found naturally in plant and animal oils and fats.
-
D-Glucose 6-phosphat...
D-Glucose 6-phosphate disodium salt is a compound widely present in biological systems. It is a molecule formed when glucose undergoes phosphorylation at the 6th carbon.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


