 Home -
Products -
Proteasome/Ubiquitin -
Endogenous Metabolite -
4-Hydroxycyclohexanecarboxylic acid
Home -
Products -
Proteasome/Ubiquitin -
Endogenous Metabolite -
4-Hydroxycyclohexanecarboxylic acid
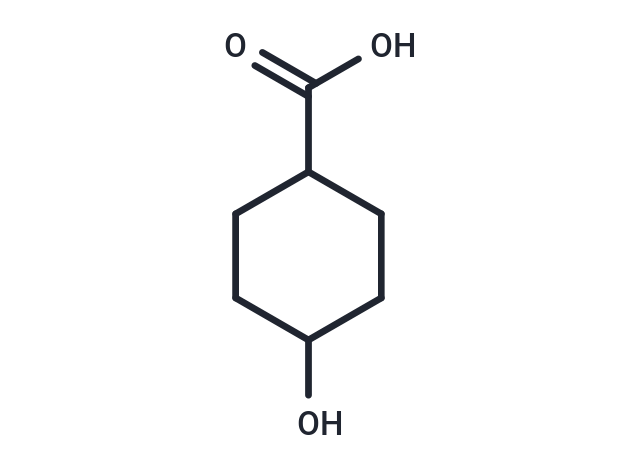
4-Hydroxycyclohexanecarboxylic acid
CAS No. 17419-81-7
4-Hydroxycyclohexanecarboxylic acid( —— )
Catalog No. M33585 CAS No. 17419-81-7
4-Hydroxycyclohexanecarboxylic acid is a substrate of cyclohexanecarboxylic acid and is isolated from olive brine.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 28 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | 27 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | 36 | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name4-Hydroxycyclohexanecarboxylic acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description4-Hydroxycyclohexanecarboxylic acid is a substrate of cyclohexanecarboxylic acid and is isolated from olive brine.
-
Description4-Hydroxycyclohexanecarboxylic acid belongs to the class of organic compounds known as cyclohexanols.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorEndogenous Metabolite
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number17419-81-7
-
Formula Weight144.17
-
Molecular FormulaC7H12O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESO=C(O)C1CCC(O)CC1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Isobutyric acid
Isobutyric acid is a carboxylic or short chain fatty acid with characteristic sweat-like smell. Small amount of isobutyrate is generated via microbial (gut) metabolism.
-
Elaidic acid
Elaidic acid is the 9-trans isomer of oleic acid. It is a monounsaturated trans-fatty acid which can be found in partially hydrogenated cooking oils.
-
17-DIMETHYLXANTHINE
Paraxanthine is a metabolite of caffeine (sc-202514) which functions as an adenosine receptor ligand and a PARP-1 inhibitor in pulmonary epithelial cells.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com

