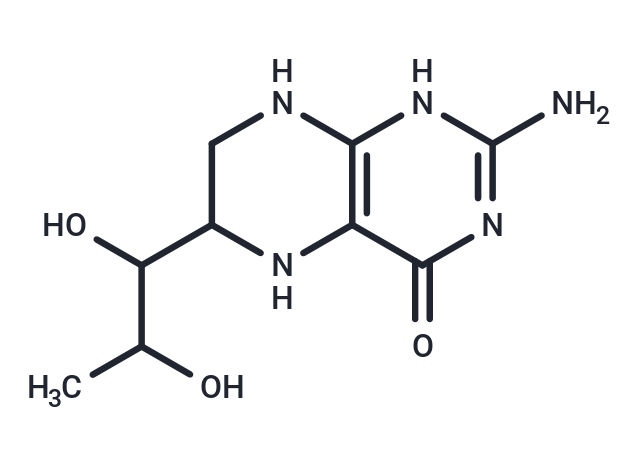
Tetrahydrobiopterin
CAS No. 17528-72-2
Tetrahydrobiopterin( —— )
Catalog No. M33520 CAS No. 17528-72-2
Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) is a cofactor for aromatic amino acid hydroxylases and an essential cofactor for nitric oxide synthase (NOS), which is used in the study of endothelial dysfunction such as hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and diabetes.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 1 mL x 10 mM in DMSO | 93 | Get Quote |


|
| 2MG | 61 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameTetrahydrobiopterin
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionTetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) is a cofactor for aromatic amino acid hydroxylases and an essential cofactor for nitric oxide synthase (NOS), which is used in the study of endothelial dysfunction such as hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and diabetes.
-
DescriptionTetrahydrobiopterin ((Rac)-Sapropterin) is a cofactor of the aromatic amino acid hydroxylases enzymes and also acts as an essential cofactor for all nitric oxide synthase (NOS) isoforms.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayProteasome/Ubiquitin
-
TargetEndogenous Metabolite
-
RecptorEndogenous Metabolite | NOS
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number17528-72-2
-
Formula Weight241.25
-
Molecular FormulaC9H15N5O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 50 mg/mL (207.25 mM; Ultrasonic )
-
SMILESCC(O)C(O)C1CNc2[nH]c(N)nc(=O)c2N1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Rivera JC, et al. Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) deficiency is associated with augmented inflammation and microvascular degeneration in the retina. J Neuroinflammation. 2017 Sep 6;14(1):181.?
molnova catalog



related products
-
3-Methyl-2-cyclopent...
3-Methyl-2-cyclopenten-1-one, used as a food additive to enhance the flavor of meat and meat products at 2-5 ppm, demonstrated gastric cytoprotective activity when administered orally to male Wistar rats.
-
Tricosanoic acid
Tricosylic acid also known as N-tricosanoate or tricosylate belongs to the class of organic compounds known as very long-chain fatty acids.
-
N-Methyl-DL-glutamic...
2-(Methylamino)pentanedioic acid (N-Methyl-DL-glutamic acid) is an endogenous metabolite that inhibits Glutaminase, adds freshness to edible products, and can be used in tuberculosis research.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


