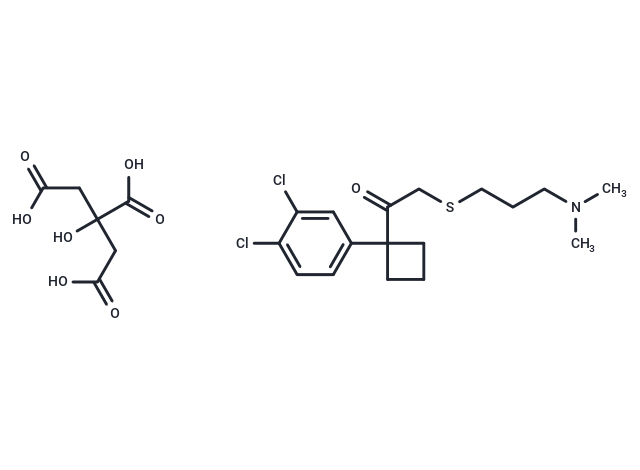
SPD-473 citrate
CAS No. 161190-26-7
SPD-473 citrate( —— )
Catalog No. M33235 CAS No. 161190-26-7
SPD-473 citrate (BTS 74398 citrate) is a dopamine reuptake inhibitor, a norepinephrine transporter protein (NET) inhibitor.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 352 | In Stock |


|
| 10MG | 495 | In Stock |


|
| 25MG | 791 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | 1042 | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | 1404 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameSPD-473 citrate
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionSPD-473 citrate (BTS 74398 citrate) is a dopamine reuptake inhibitor, a norepinephrine transporter protein (NET) inhibitor.
-
DescriptionSPD-473 citrate is a serotonin/dopamine/norepinephrine reuptake inhibitior.
-
In VitroSPD-473 inhibits the synaptic reuptake of dopamine, serotonin and noradrenaline, making it a triple reuptake inhibitor potentially for the treatment of Parkinson's Disease.
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayGPCR/G Protein
-
TargetDopamine Receptor
-
RecptorDopamine Receptor | 5-HT Receptor | Norepinephrine
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number161190-26-7
-
Formula Weight552.47
-
Molecular FormulaC23H31Cl2NO8S
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESO=C(O)CC(O)(C(=O)O)CC(=O)O.O=C(CSCCCN(C)C)C1(C2=CC=C(Cl)C(Cl)=C2)CCC1
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Acetophenazine dimal...
Acetophenazine dimaleate is an antipsychotic agent, effective in anxious depression. Acetophenazine dimaleate primarily targets the dopamine D2 receptor.
-
Rotigotine
A non-selective agonist of the dopamine D3 receptor (Ki=0.71 nM); has 10-fold selectivity for the D3 receptor over the D2, D4, and D5 receptors and 100-fold selectivity for the D3 receptor over the D1 receptor.
-
Seridopidine
Seridopidine (ACR343) is a modulator of dopaminergic activity that is used as an oral therapy for schizophrenia, Parkinson's disease, and Tourette's syndrome.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


